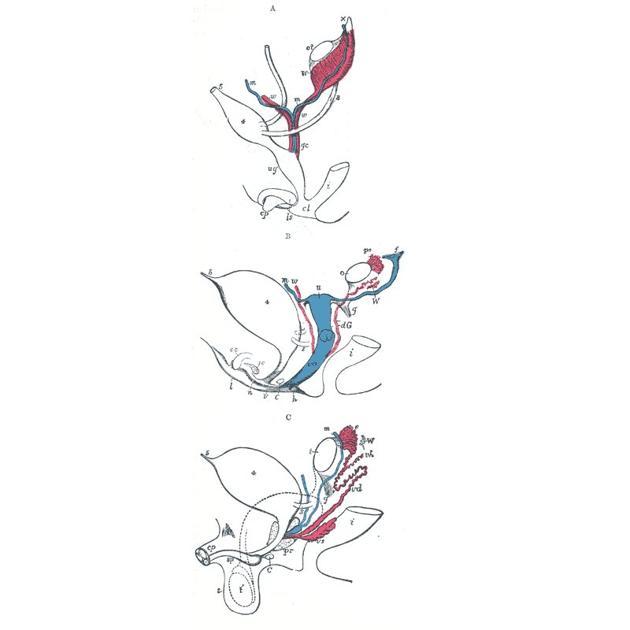
Müllerian duct
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Paramesonephric ducts
- Müllerian ducts
The Müllerian ducts (or paramesonephric ducts) are paired ducts of mesodermal origin in the embryo. They run laterally down the side of the urogenital ridge and terminate at the Müllerian eminence in the primitive urogenital sinus.
In the female, they will develop to form the uterine tubes, uterus, and the upper portion of the vagina; in the male, the vestigial remnant is the appendix testis.
On this page:
History and etymology
They are named after Johannes Peter Müller (1801-1858), a pioneering German physiologist and comparative anatomist who described these ducts in his text "Bildungsgeschichte der Genitalien" in 1830.
Related pathology
See also
References
- 1. Lohff B. Johannes Muller and the beginnings of experimental neurophysiology: concepts and strategies. (1999) Physis; rivista internazionale di storia della scienza. 36 (2): 339-54. Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Uterus didelphys
- Longitudinal vaginal septum
- Prostatic utricle
- Bicornuate uterus
- Müllerian duct anomalies
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome
- Uterine agenesis
- Müllerian duct anomaly classification
- Cervical plicae palmatae
- Müllerian duct cyst
- Transverse vaginal septum
- Unicornuate uterus
- Vagina
- Testicular appendix
- Persistent Müllerian duct syndrome
- Sexual differentiation
- Wolffian duct
- Ureteric bud
- Testicular appendages
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract[+][+]
- spleen[+][+]
- hepatobiliary system[+][+]
-
endocrine system[+][+]
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system[+][+]
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system[+][+]
- female reproductive system
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics[+][+]
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses