Neural tube
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Michelle P had no recorded disclosures.
View Michelle P's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures- Neural tubes
The neural tube comprises of a bundle of nerve sheaths and is the embryonic structure that ultimately forms the primitive brain at the cranial end and the spinal cord at the caudal end 1,2.
The neural tube is formed during an embryological process called neurulation, a folding process where the neural plate transforms into the neural tube 1. The centre of the tube is the neural canal 2. Neurulation starts at approximately day 20 after fertilisation and is completely closed by approximately day 29 1,2,4.
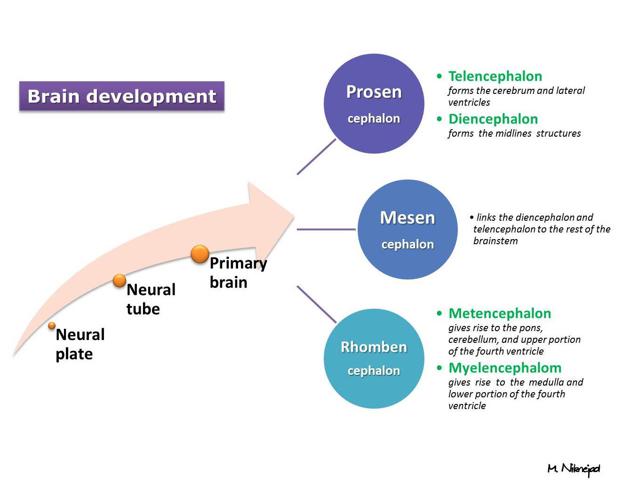
There are distinct vesicles which make up the neural tube 2. Each of these subdivisions develops into distinct regions of the central nervous system, resulting in brain development 1-3:
-
prosencephalon (forebrain) 1,2
eventually develops into the telencephalon and diencephalon
-
rhombencephalon (hindbrain) 1,2
eventually develops into the metencephalon and myelencephalon
spinal cord 1,2
When the primary vesicles of the brain are formed, they can be recognised with endovaginal sonography.
Related pathology
Failure of neural tube closure in early pregnancy can result in neural tube defects, one of the commonest and most severe malformations of the fetus and newborn 3,4.
References
- 1. Copp A & Greene N. Genetics and Development of Neural Tube Defects. J Pathol. 2010;220(2):217-30. doi:10.1002/path.2643 - Pubmed
- 2. Sequerra E, Goyal R, Castro P, Levin J, Borodinsky L. NMDA Receptor Signaling Is Important for Neural Tube Formation and for Preventing Antiepileptic Drug-Induced Neural Tube Defects. J Neurosci. 2018;38(20):4762-73. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2634-17.2018 - Pubmed
- 3. Sadler T. Embryology of Neural Tube Development. American J of Med Genetics Pt C. 2005;135C(1):2-8. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.30049 - Pubmed
- 4. Nikolopoulou E, Galea G, Rolo A, Greene N, Copp A. Neural Tube Closure: Cellular, Molecular and Biomechanical Mechanisms. Development. 2017;144(4):552-66. doi:10.1242/dev.145904 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Neural plate
- Myelomeningocele
- Midbrain
- Rachischisis totalis
- Caudal regression syndrome
- Myelencephalon
- Spina bifida occulta
- Quadrigeminal plate
- Spina bifida
- Prosencephalon
- Anencephaly
- Central nervous system embryology
- Brain development
- Neural tube defects
- Somite
- Ventricular system
- Lipomyelocele
- Spinal dysraphism
- Rhombencephalon
- Central canal
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.