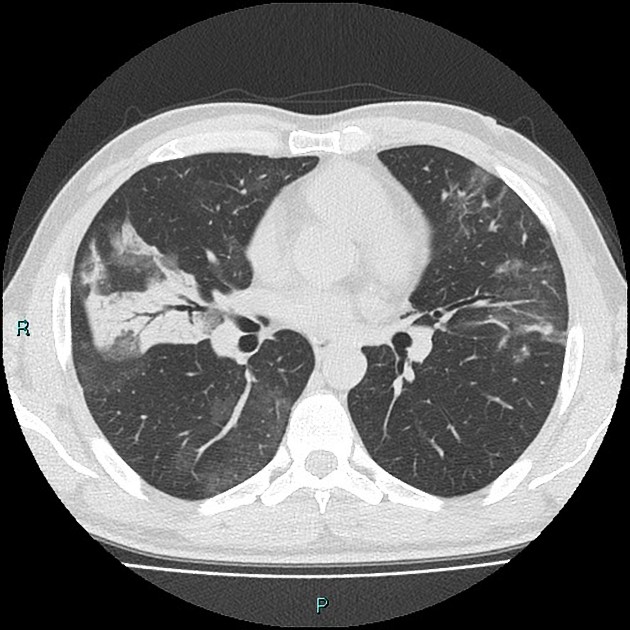
Organising pneumonia (OP) refers to a clinicopathological entity which is associated with non-specific clinical findings, radiographic findings, and pulmonary function test (PFT) results.
When an underlying cause is unknown it is classified as cryptogenic organising pneumonia (COP; also referred to as primary organising pneumonia) whereas if a cause is known it is then termed a secondary organising pneumonia.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Most cases of organising pneumonia (50-70%) are classified as cryptogenic 5,6.
Pathology
Microscopic appearance
Organising pneumonia comprises a histological pattern characterised by granulation tissue polyps within alveolar ducts and alveoli and with chronic inflammation involving the adjacent lung parenchyma.
Treatment and prognosis
Most (especially cryptogenic forms) respond very well to corticosteroid treatment; however, a small percentage of patients may develop progressive fibrosis - fibrosing organising pneumonia 7.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.