Pancreatic trauma injury grading
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- Pancreatic trauma grading
- Grading of pancreatic trauma
- Grading of pancreatic injury
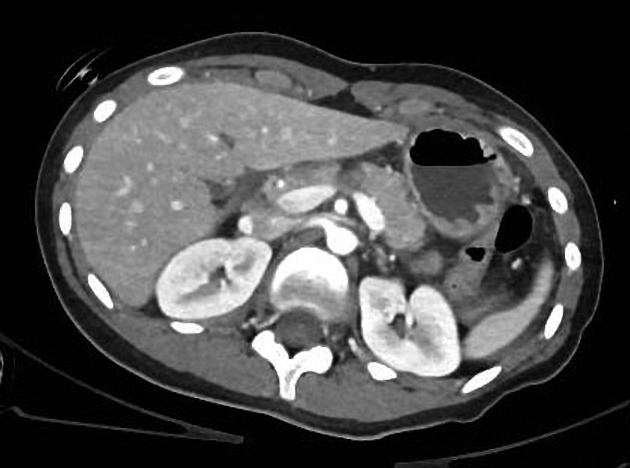
Several pancreatic injury grading systems have been proposed for pancreatic trauma.
Classifications
American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST)
The proximal pancreas is defined as the gland to the right of the superior mesenteric vein (SMV)-portal vein axis, whereas the distal pancreas is to the left of the axis. The term deep refers to an injury down to the level of the duct, whereas superficial implies the injury is superficial to the duct 7.
AAST grading is as follows 5,7:
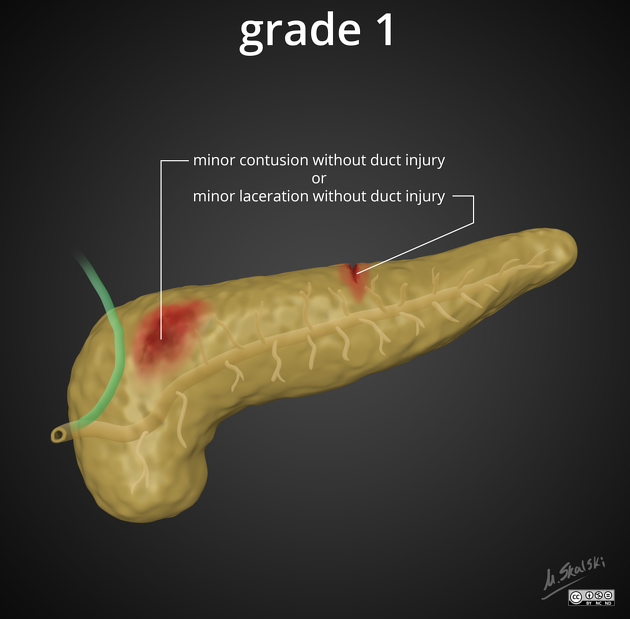
grade I: haematoma with minor contusion or superficial laceration without duct injury
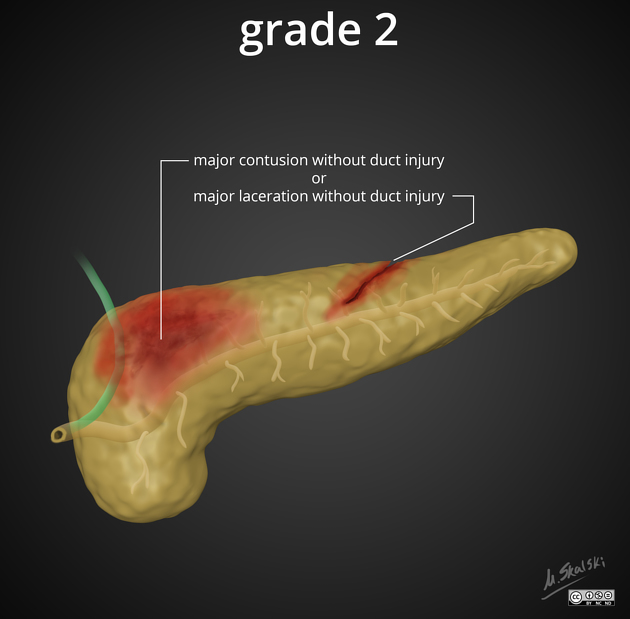
grade II: major contusion or laceration without duct injury
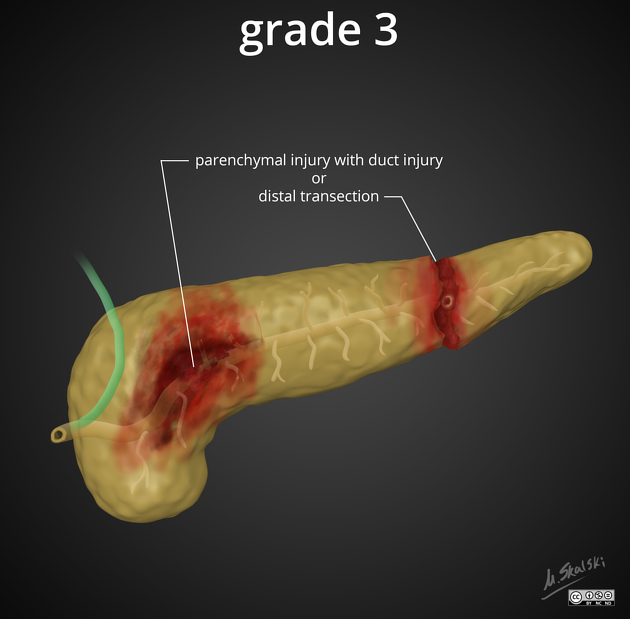
grade III: distal transection or deep parenchymal injury with duct injury
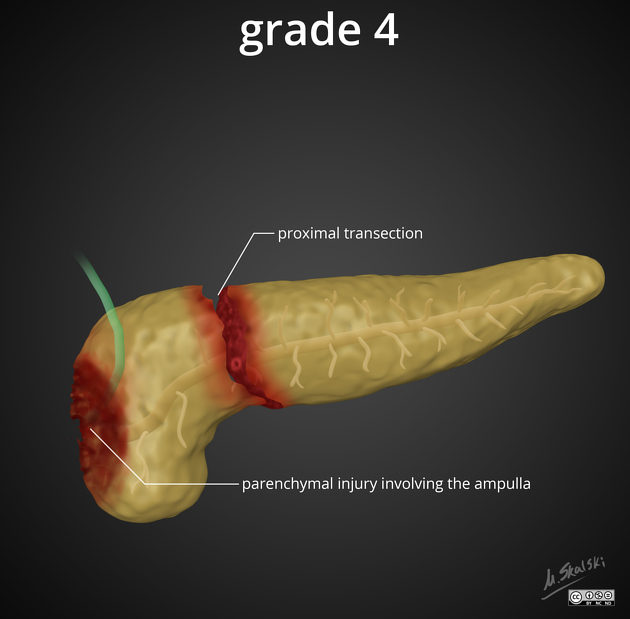
grade IV: proximal transection or deep parenchymal injury involving the ampulla (and/or intrapancreatic common bile duct)
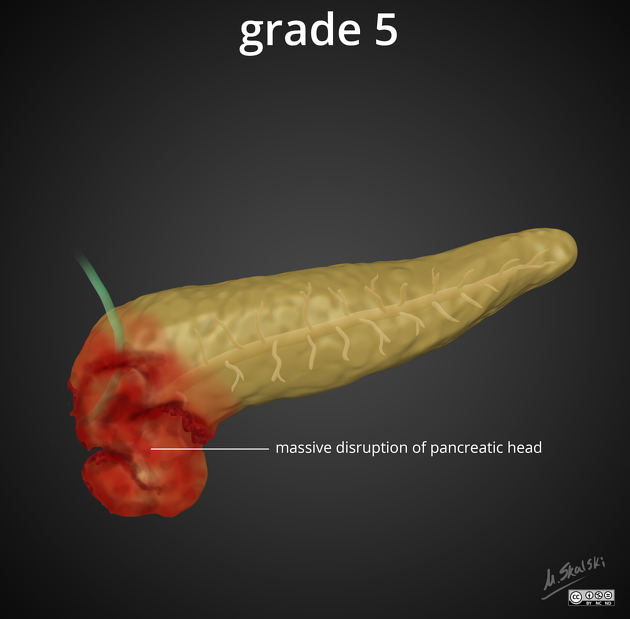
grade V: massive disruption of the pancreatic head ("shattered pancreas")
NB advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade 3.
Grades I and II do not involve the duct and are considered low-grade injuries. Grades III, IV and V involve the duct and constitute "high-grade" injuries ref.
Wong et al. 3
A more simple method for grading severity on CT in pancreatic injury proposed by Wong et al. 3 is:
grade A: pancreatitis or superficial laceration only
-
grade B
BI: deep laceration involving pancreatic tail
BII: complete transection of pancreatic tail
-
grade C
CI: deep laceration involving pancreatic head
CII: complete transection of pancreatic head
References
- 1. Linsenmaier U, Wirth S, Reiser M, Körner M. Diagnosis and Classification of Pancreatic and Duodenal Injuries in Emergency Radiology. Radiographics. 2008;28(6):1591-602. doi:10.1148/rg.286085524 - Pubmed
- 2. Wong Y, Wang L, Chen R, Chen C. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Extrahepatic Bile Duct Disruption. Eur Radiol. 2002;12(10):2488-90. doi:10.1007/s00330-001-1296-8 - Pubmed
- 3. Wong Y, Wang L, Lin B, Chen C, Lim K, Chen R. CT Grading of Blunt Pancreatic Injuries: Prediction of Ductal Disruption and Surgical Correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1997;21(2):246-50. doi:10.1097/00004728-199703000-00014 - Pubmed
- 4. Oniscu G, Parks R, Garden O. Classification of Liver and Pancreatic Trauma. HPB (Oxford). 2006;8(1):4-9. doi:10.1080/13651820500465881 - Pubmed
- 5. American Association for the Surgery of Trauma: Injury Scoring Scale
- 6. Ayoob A, Lee J, Herr K et al. Pancreatic Trauma: Imaging Review and Management Update. Radiographics. 2021;41(1):58-74. doi:10.1148/rg.2021200077 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Pancreatic trauma
- Pancreatic trauma with posttraumatic pseudocyst and ductal injury
- Pancreatic transection
- Pancreatic trauma - ultrasound
- Pediatric pancreatic laceration (grade III injury)
- Pancreatic trauma
- Isolated pancreatic laceration in a paediatric patient with closed abdominal trauma
- Pancreatic transection
- Pancreatic trauma
- Pancreatic trauma (grade III)
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (unresectable)
- Pancreatic trauma grading (diagrams)
- Pancreatic laceration
- Pancreatic laceration
- Fallen lung, pneumothorax, hepatic and pancreatic lacerations and retroperitoneal haematoma
- Traumatic renal artery dissection and pancreatic transection
- Ligated splenic artery and vein post pancreatectomy for traumatic pancreatic transection
- Polytrauma with left renal devascularization, pancreatic transection, splenic and hepatic lacerations
- Polytrauma with hepatic lacerations and haemoperitoneum
- Pancreatic trauma
Related articles: Trauma scoring
-
AAST injury scores
- liver injury grading
- renal injury grading
- splenic injury grading
- pancreatic injury grading
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- benign epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumours
- primary malignant epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumours
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumours
- haematopoietic and lymphoid tumours
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumours
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumours
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic haemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumour
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumour
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumour
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour (inflammatory pseudotumour)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumours
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumours
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridaemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.