Photon starvation
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created shariq ahmad shah had no recorded disclosures.
View shariq ahmad shah's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
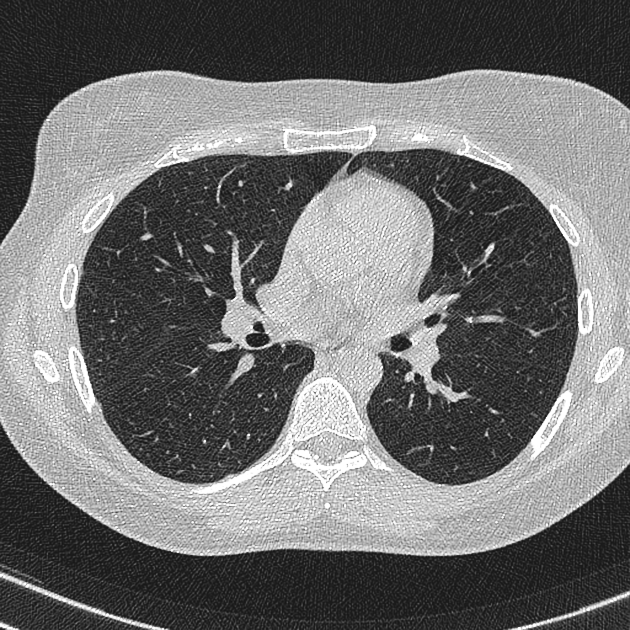
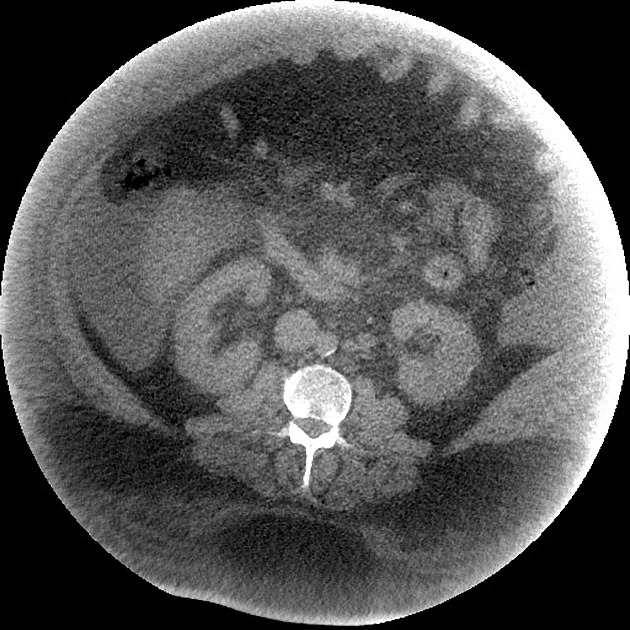
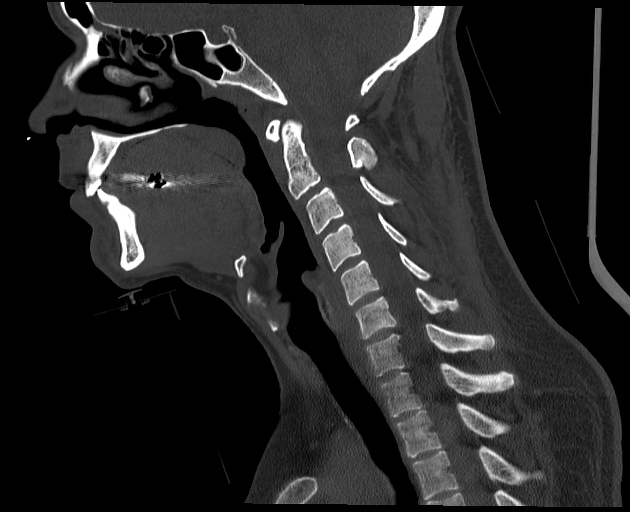
View Arlene Campos's current disclosuresPhoton starvation is one source of streak artifact which may occur in CT. It is seen in high attenuation areas, particularly behind metal implants. Because of high attenuation, insufficient photons reach the detector. During the reconstruction process, the noise is greatly magnified in these areas leading to characteristic streaks in the image 3.
In some applications, namely low dose CT protocols, the increased noise due to photon starvation is normally encountered as a trade-off between low patient radiation dose and acceptable image quality. The artifact can be reduced by automatic tube current modulation (increased mAs) and adaptive filtration via applying the local filter. Use of iterative reconstruction techniques can also significantly reduce image noise caused by this artifact 2,3.
References
- 1. Barrett J & Keat N. Artifacts in CT: Recognition and Avoidance. Radiographics. 2004;24(6):1679-91. doi:10.1148/rg.246045065 - Pubmed
- 2. Triche B, Nelson J, McGill N et al. Recognizing and Minimizing Artifacts at CT, MRI, US, and Molecular Imaging. Radiographics. 2019;39(4):1017-8. doi:10.1148/rg.2019180022 - Pubmed
- 3. Hao S, Liu J, Chen Y et al. A Wavelet Transform-Based Photon Starvation Artifacts Suppression Algorithm in CT Imaging. Phys Med Biol. 2020;65(23):235039. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/abb171 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Computed tomography
- computed tomography in practice
-
computed tomography overview
- iodinated contrast media
- CT IV contrast media administration
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT technology
-
generations of CT scanners
- helical CT scanning
- step and shoot scanning
- ultra-high-resolution CT (UHRCT)
- CT x-ray tube
- CT fluoroscopy
- cone-beam CT
-
generations of CT scanners
- dual-energy CT
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT protocols
- composite
- head & neck
- chest
- abdomen and pelvis
- CT abdomen-pelvis (protocol)
- CT abdominal aorta
- CT adrenals (protocol)
- CT cholangiography (protocol)
- CT colonography (protocol)
- CT enteroclysis (protocol)
- CT enterography (protocol)
- CT gastrography (protocol)
- CT kidneys, ureters and bladder (protocol)
- CT urography (protocol)
- CT Renal mass (protocol)
- CT angiography of the splanchnic vessels (protocol)
- CT renal split bolus
- CT pancreas (protocol)
- liver




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.