Platybasia is characterised by abnormal flattening of the skull base as defined as a base of skull angle over 143º.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Platybasia alone does not usually cause symptoms unless it is associated with basilar invagination 6.
Pathology
Aetiology
- congenital
- acquired
Associations
Radiographic features
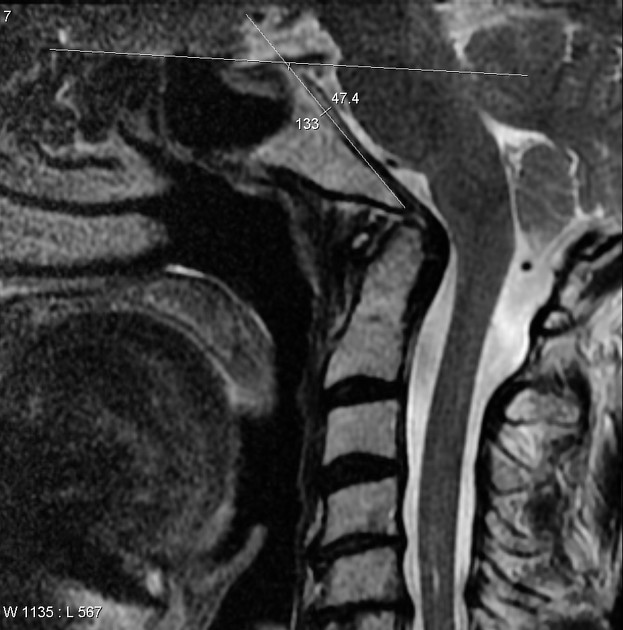
A number of techniques have been described to measure platybasia 1.
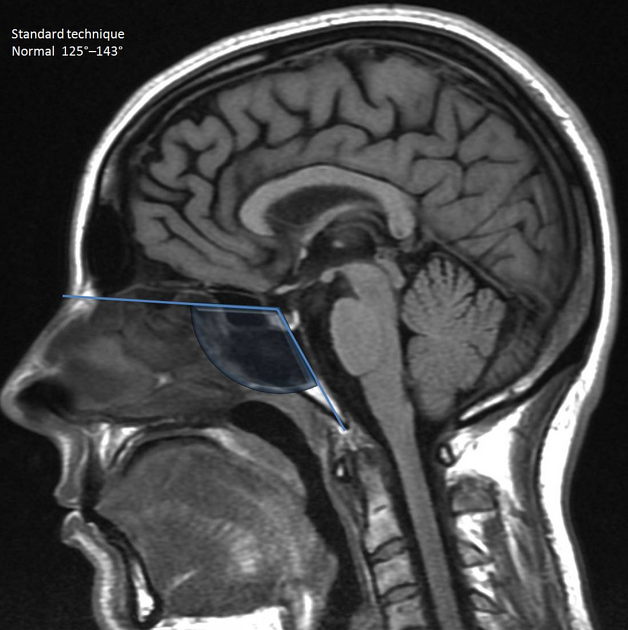
- standard measurement: the angle formed by a line joining the nasion with the centre of the pituitary fossa and a line joining the anterior border of the foramen magnum with the centre of the pituitary fossa 1
- normal 125°–143°
- platybasia >143°
- basilar kyphosis <125°
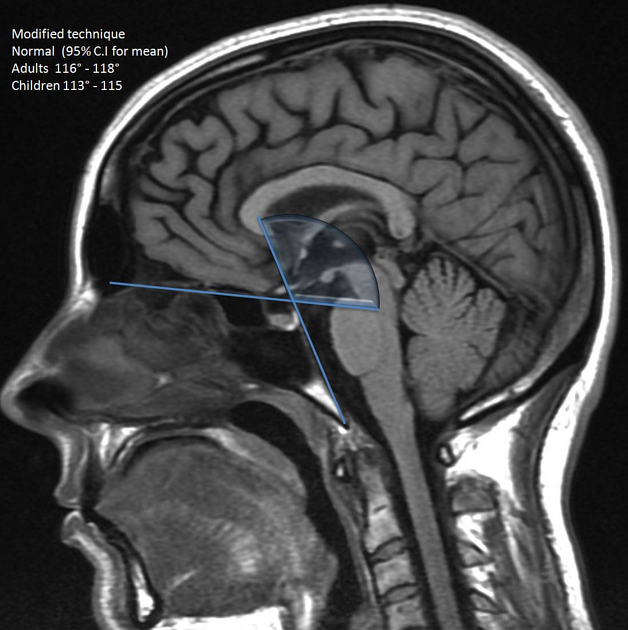
- modified measurement: the angle formed by a line extending across the anterior cranial fossa to the tip to the dorsum sellae and a line drawn along the posterior margin of the clivus 1
- adult normal value range: 116°-118°
- children normal range: 113°-115°





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.