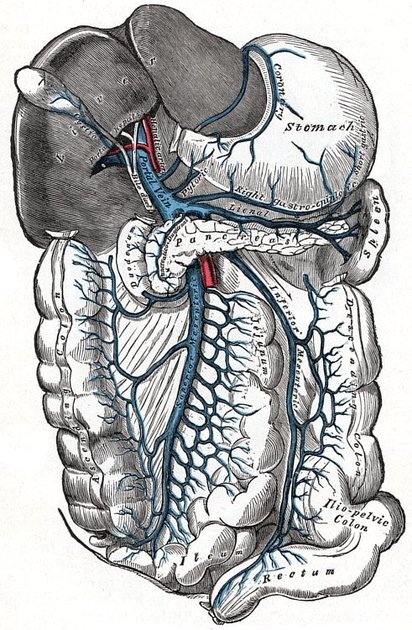
Portal venous system
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Amir Mahmud had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Amir Mahmud's current disclosures- Portal systems (disambiguation)
- Portal vein systems
- Portal venous systems
The portal venous system refers to the vessels involved in the drainage of the capillary beds of the GI tract and spleen into the capillary bed of the liver.
Blood flow to the liver is unique in that it receives both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. As a result, the partial pressure of oxygen (pO2) and perfusion pressure of portal blood are lower than in other organs of the body. Blood passes from branches of the portal vein through cavities between hepatocellular sinusoids. Blood also flows from branches of the hepatic artery and mixes in the sinusoids to supply the hepatocytes with oxygen. This mixture percolates through the sinusoids and collects in a central vein which drains into the hepatic veins. The hepatic veins subsequently drain into the inferior vena cava.
In infants and young children, valves are present within the portovenous system. However, such valves regress during adulthood.
Terminology
A portal venous system is one in which veins connect two capillary beds; or in other words drain one organ/organ system and pass into another organ/organ system rather than being directly returned to the heart. The hepatic portal vein is the only portal system many are aware of. However, there is also a hypophyseal portal system which passes blood from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary 1. Therefore, strictly speaking the system draining the GI tract and passing to the liver should be termed the hepatic portal venous system to distinguish it from the less well-known hypothalamic-pituitary portal system.
References
- 1. Gray's Anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0443066841. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2011) Page 193. ISBN: 9780702029714 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera[+][+]
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries[+][+]
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins[+][+]
- anastomoses[+][+]
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries[+][+]
- lymphatics[+][+]
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses