Posterior longitudinal ligament
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Wong A, Hacking C, Gaillard F, et al. Posterior longitudinal ligament. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 24 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-36586
rID:
36586
Article created:
30 Apr 2015,
Aaron Wong
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Aaron Wong had no recorded disclosures.
View Aaron Wong's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures
Revisions:
7 times, by
6 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Synonyms:
- Posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL)
- Posterior longitudinal ligaments
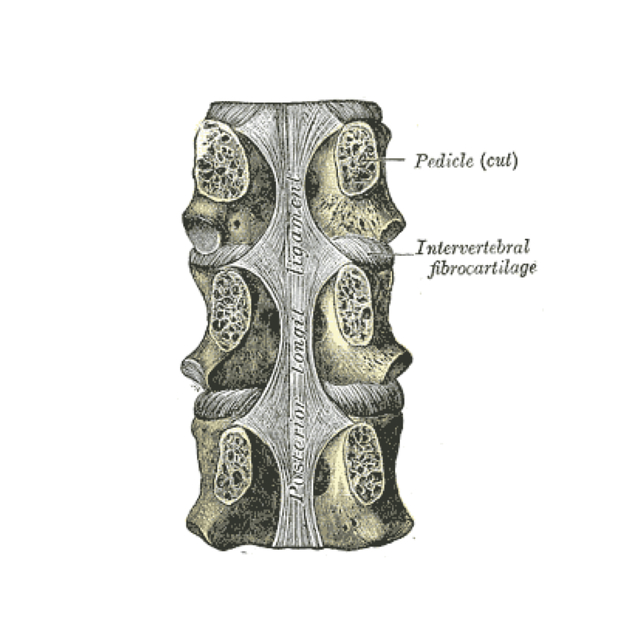
The posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) is a long and important ligament located immediately posterior to the vertebral bodies (to which it attaches loosely) and intervertebral discs (to which it is firmly attached).
It extends from the back of the sacrum inferiorly and gradually broadens as it ascends. At the level of C2 (the axis) it spreads out and becomes the tectorial membrane that eventually inserts into the base of skull 1,2.
References
- 1. McMINN. Lasts Anatomy Regional and Applied. CHURCHILL LIVINGSTONE. (2003) ISBN:B0084AQDG8. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Walter Carl Hartwig. Fundamental Anatomy. (2018) ISBN: 9780781768887
Incoming Links
Articles:
- Curtain sign (vertebral body mass)
- Infantile cervical ligament oedema
- Intervertebral joint
- Anterior meningeal artery
- Symphysis
- Tectorial membrane of the spine
- Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
- Spinal canal
- Lumbar spine
- Discoligamentous injury
- Sinuvertebral nerve
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (P)
- Cervical spine ligaments
- Spinal epidural space
- Spinal meninges
- Subaxial cervical spine injury classification
- Three column concept of spinal fractures
- Disc herniation
- Discectomy
Related articles: Anatomy: Spine
-
osteology
- vertebrae
- spinal canal
- cervical spine
- thoracic spine
- lumbar spine
- sacrum
- coccyx
-
anatomical variants
- vertebral body
- neural arch
- transitional vertebrae
- ossicles
- ossification centres
- intervertebral disc
- articulations
- ligaments
- musculature of the vertebral column
- muscles of the neck
- muscles of the back
-
suboccipital muscle group
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- splenius capitis muscle
- splenius cervicis muscle
- erector spinae group
- transversospinalis group
- quadratus lumborum muscle
-
suboccipital muscle group
- spinal meninges and spaces
-
spinal cord
- gross anatomy
-
white matter tracts (white matter)
- corticospinal tract
- anterolateral columns
- lateral columns
-
dorsal columns
- fasiculus gracilis (column of Goll)
- fasiculus cuneatus (column of Burdach)
- grey matter
- nerve root
- central canal
- functional anatomy
- spinal cord blood supply
- sympathetic chain






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.