Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Jones J, Knipe H, Silverstone L, et al. Pulmonary nodule. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 30 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-10187
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (past)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to
not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures
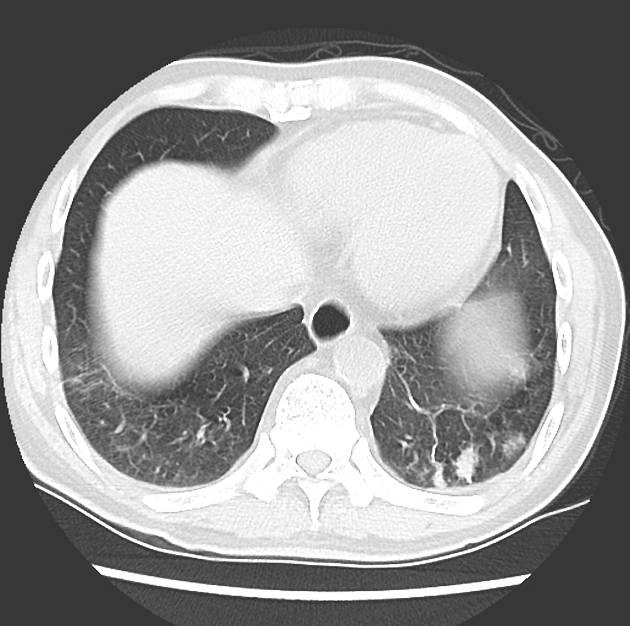
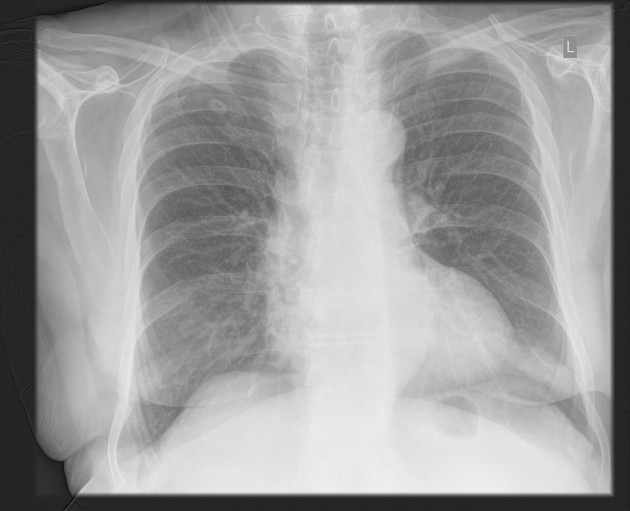
Pulmonary nodules are small, rounded opacities within the pulmonary interstitium. Pulmonary nodules are common, and as the spatial resolution of CT scanners has increased, the detection of smaller and smaller nodules has occurred, which are more often an incidental finding.
Pulmonary nodules can be described according to size, morphology and/or distribution.
Size
Morphology
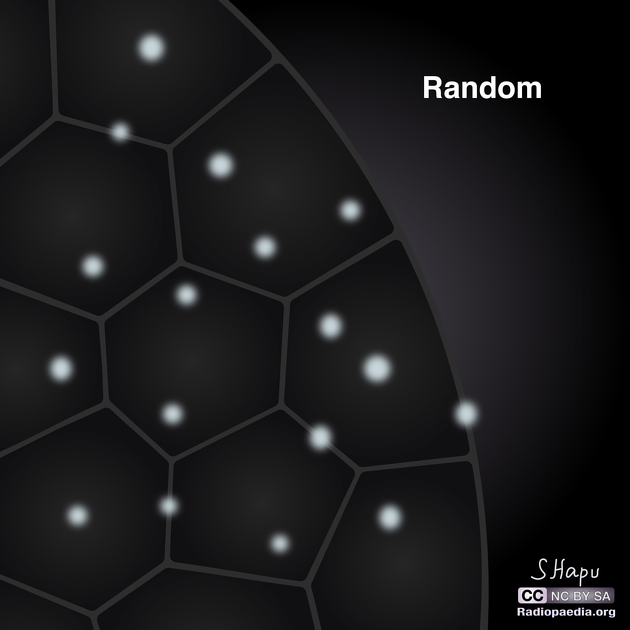
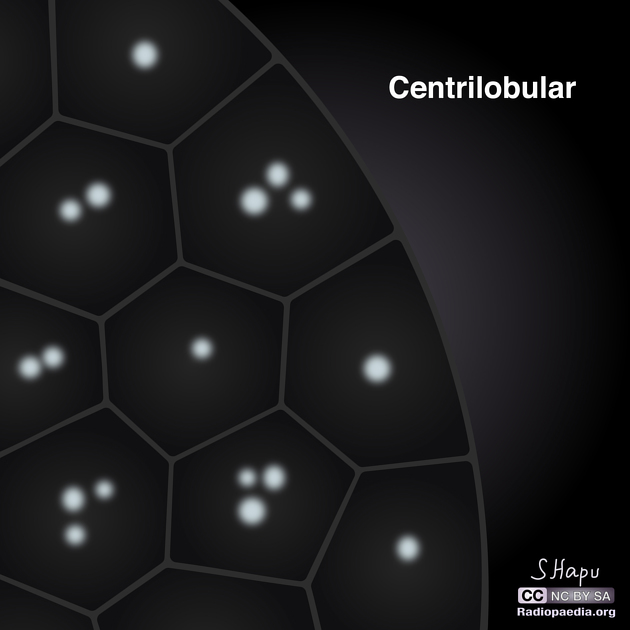
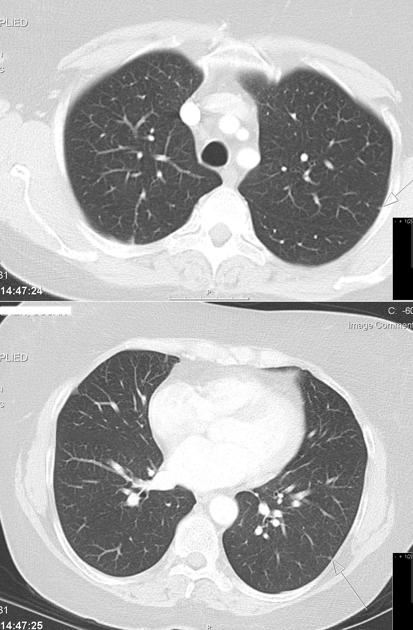
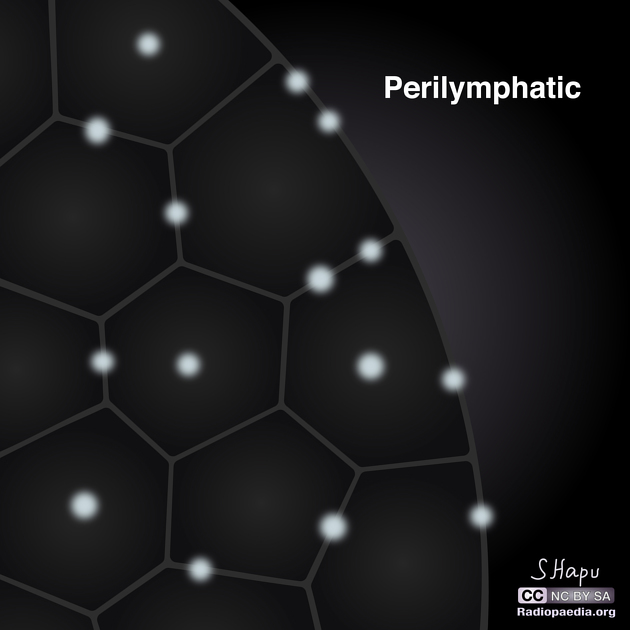
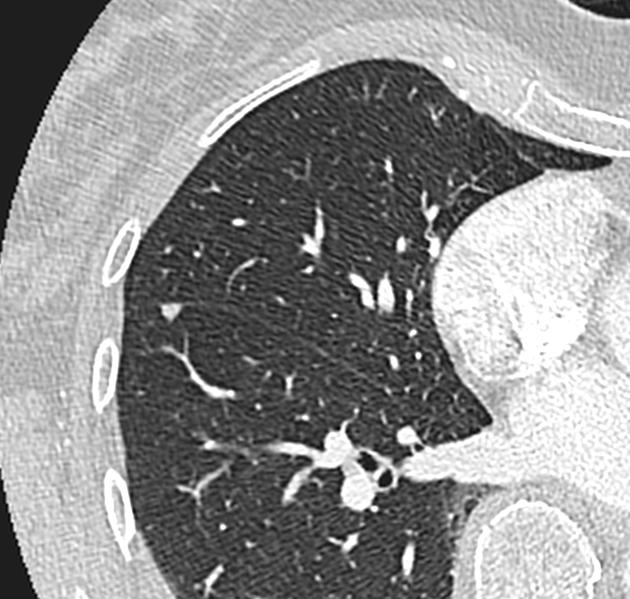
Distribution
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
They are generally homogeneous (without air bronchograms or alveolograms) and are well-defined since their margins are sharp and they are surrounded by normally aerated lung parenchyma. They are quite separate from airspace nodules that often have an irregular margin and are usually ~8 mm in diameter. (For further discussion, see the article on nodular opacification.)
The differential diagnosis for a nodule can be refined by its size, location, and density. Solitary pulmonary nodules and hyperdense pulmonary nodules are discussed further elsewhere.
A micronodular or miliary pattern is predominately seen in granulomatous processes, haematogenous pulmonary metastases, and pneumoconioses. Nodules and masses are most often seen in metastatic disease to the lung.
Always be aware of artifacts, especially on radiographs, where buttons or nipple shadows can often be mistaken for a true pulmonary nodule 7.
The term micronodule has been defined variably by different position statements. In the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) all nodules with <4 mm maximum diameter were recorded as micronodules 8. Some authors consider lesions measuring <3 mm as micronodules 9. In this article, we follow the cutoff recommended by the Fleischner Glossary published in 2024 which classifies nodules <6 mm as micronodules, which are generally ‘non-actionable’ 11.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
-
1. Boitsios G, Bankier A, Eisenberg R. Diffuse Pulmonary Nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194(5):W354-66. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.4345 - Pubmed
-
2. MacMahon H, Austin J, Gamsu G et al. Guidelines for Management of Small Pulmonary Nodules Detected on CT Scans: A Statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology. 2005;237(2):395-400. doi:10.1148/radiol.2372041887 - Pubmed
-
3. Prosch H, Strasser G, Oschatz E, Schober E, Schneider B, Mostbeck G. Management of Patients with Small Pulmonary Nodules: A Survey of Radiologists, Pulmonologists, and Thoracic Surgeons. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187(1):143-8. doi:10.2214/AJR.05.1229 - Pubmed
-
4. Gould M, Donington J, Lynch W et al. Evaluation of Individuals with Pulmonary Nodules: When is It Lung Cancer? Diagnosis and Management of Lung Cancer, 3rd Ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 Suppl):e93S-e120S. doi:10.1378/chest.12-2351 - Pubmed
-
5. Snoeckx A, Reyntiens P, Desbuquoit D et al. Evaluation of the Solitary Pulmonary Nodule: Size Matters, but Do Not Ignore the Power of Morphology. Insights Imaging. 2018;9(1):73-86. doi:10.1007/s13244-017-0581-2 - Pubmed
-
6. Raad R, Suh J, Harari S, Naidich D, Shiau M, Ko J. Nodule Characterization: Subsolid Nodules. Radiol Clin North Am. 2014;52(1):47-67. doi:10.1016/j.rcl.2013.08.011 - Pubmed
-
7. Dr Stephen Ellis. Interpreting Chest X Rays. (2010) ISBN: 9781904842774 - Google Books
-
8. Munden R, Chiles C, Boiselle P, Sicks J, Aberle D, Gatsonis C. Micronodules Detected on Computed Tomography During the National Lung Screening Trial: Prevalence and Relation to Positive Studies and Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(9):1538-46. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2019.05.045 - Pubmed
-
9. Sánchez M, Benegas M, Vollmer I. Management of Incidental Lung Nodules <8 Mm in Diameter. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10(Suppl 22):S2611-27. doi:10.21037/jtd.2018.05.86 - Pubmed
-
10. Bankier A, MacMahon H, Goo J, Rubin G, Schaefer-Prokop C, Naidich D. Recommendations for Measuring Pulmonary Nodules at CT: A Statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology. 2017;285(2):584-600. doi:10.1148/radiol.2017162894 - Pubmed
-
11. Bankier A, MacMahon H, Colby T et al. Fleischner Society: Glossary of Terms for Thoracic Imaging. Radiology. 2024;310(2):e232558. doi:10.1148/radiol.232558 - Pubmed
Multiple choice questions:
Promoted articles (advertising)





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.