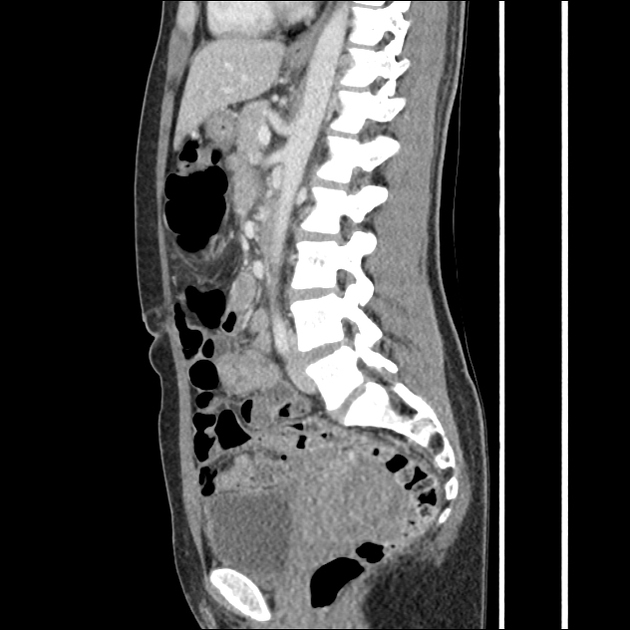
Retroaortic left renal vein
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mohammad Taghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mohammad Taghi Niknejad's current disclosures- Retroaortic left renal vein
- Retro aortic left renal vein (RLRV)
- Retro-aortic left renal vein (RLRV)
- Retro aortic left renal vein
- Retroaortic left renal vein (RLRV)
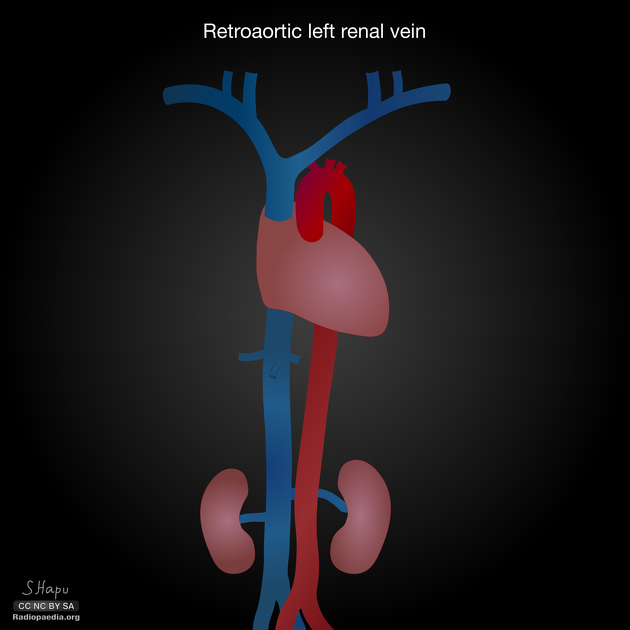
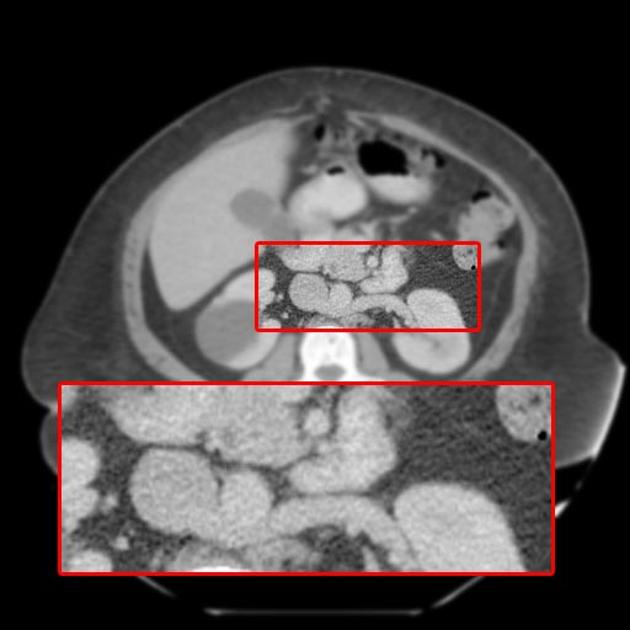
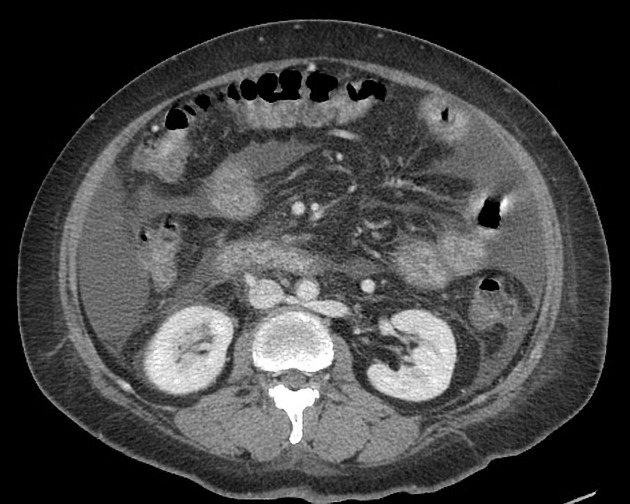
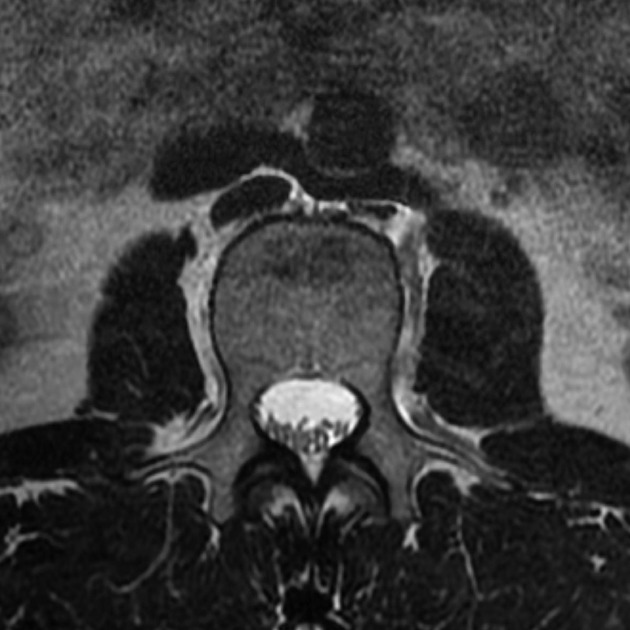
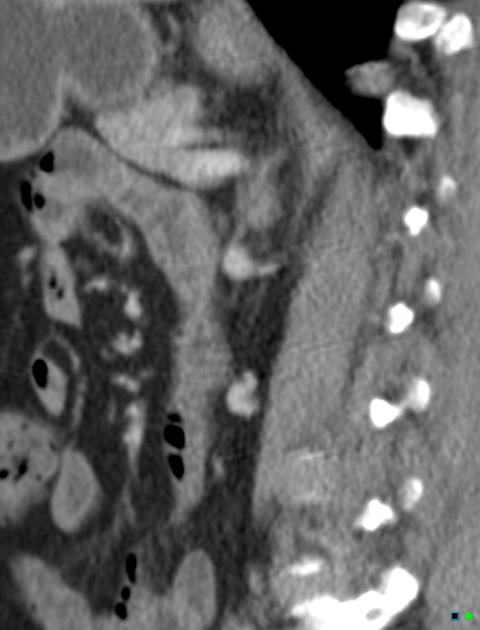
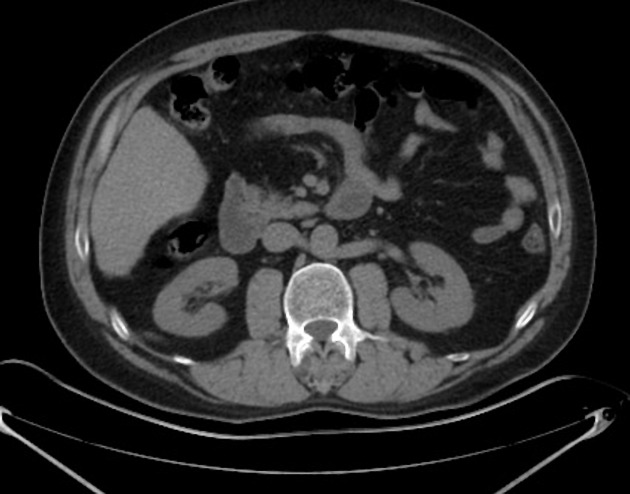
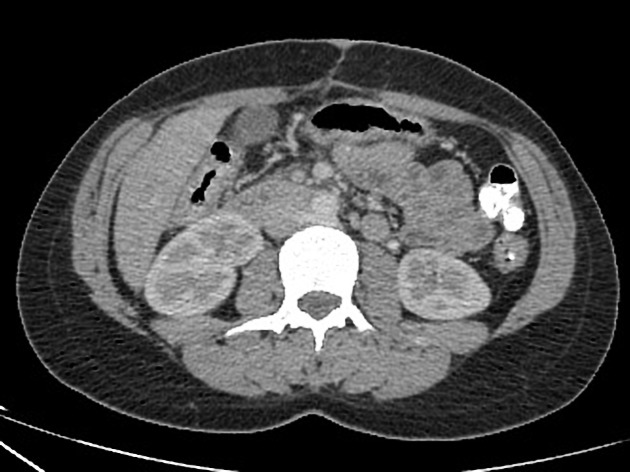
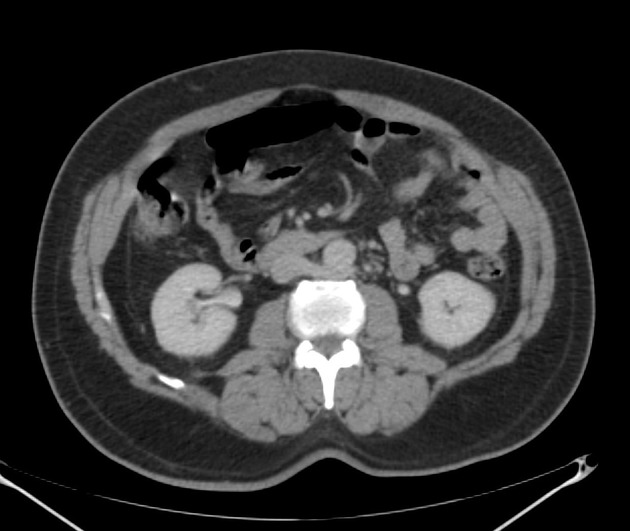
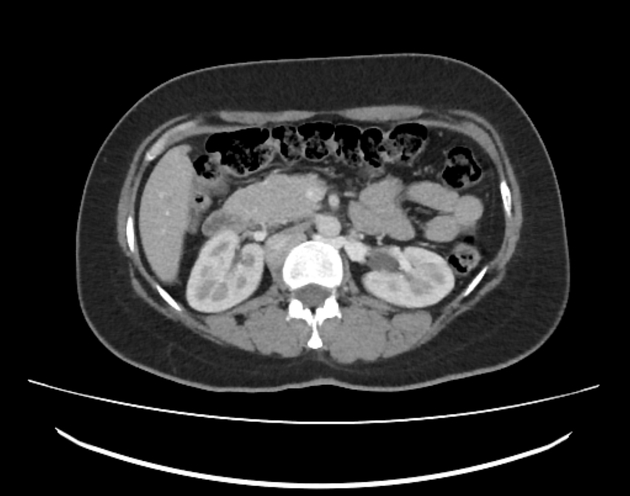
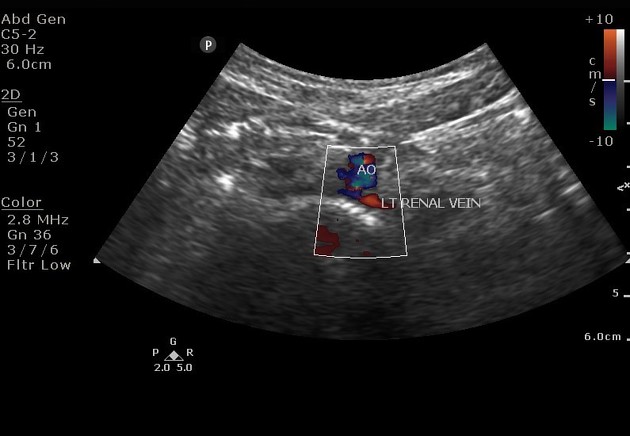
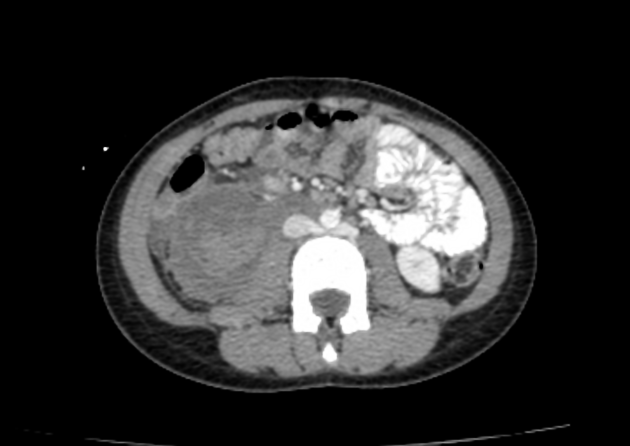
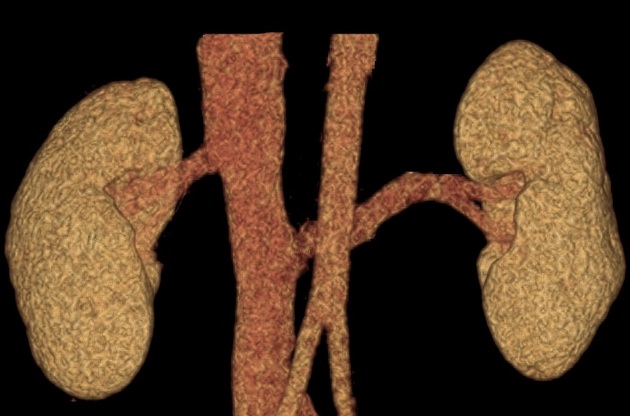
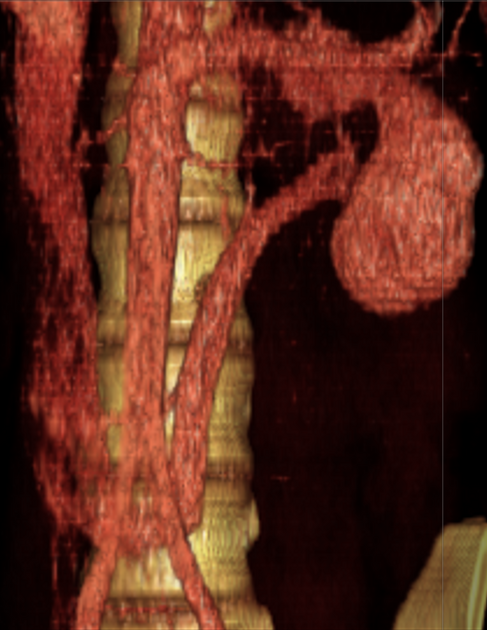
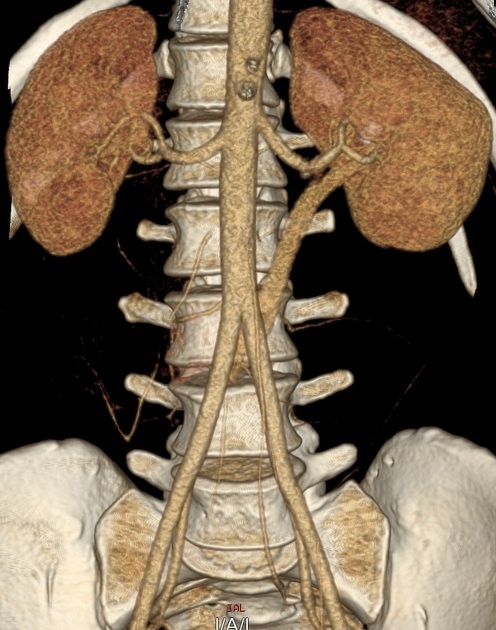
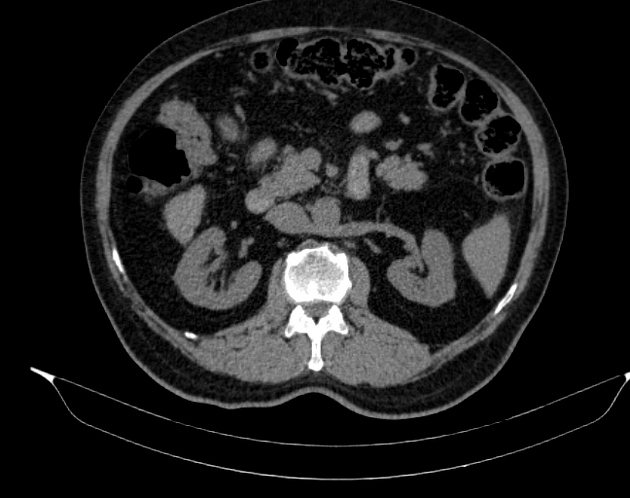
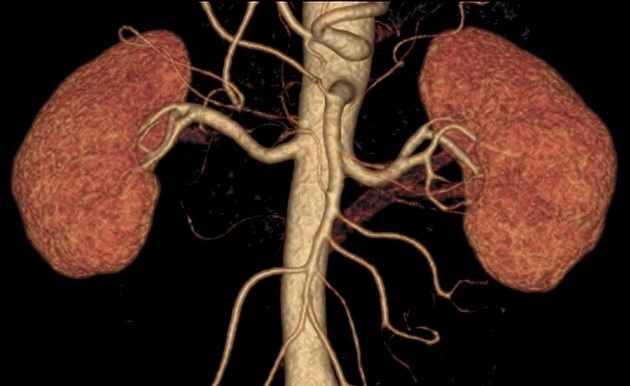
Retroaortic left renal vein (RLRV) is a normal anatomical variant where the left renal vein is located between the aorta and the vertebra and drains into the inferior vena cava.
Its recognition is important to avoid complications during retroperitoneal surgery or interventional procedures 2.
On this page:
Images:
Epidemiology
Retroaortic left renal vein has an estimated prevalence of ~2% 3.
Clinical presentation
Urological symptoms can be caused by increased pressure in the renal vein, which can result in venous hypertension. This is an atypical form of nutcracker syndrome. Patients can present with hematuria and recurrent left flank pain.
Types
The retroaortic position of the left renal vein has four subtypes 4:
RLRV joining the IVC in the normal position
RLRV joining the IVC at the level of L4–5
circumaortic or collar LRV, having two limbs, one crossing anterior and one behind the aorta
RLRV drains into the left common iliac vein
References
- 1. Nam JK, Park SW, Lee SD et-al. The clinical significance of a retroaortic left renal vein. Korean J Urol. 2010;51 (4): 276-80. doi:10.4111/kju.2010.51.4.276 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 2. Karaman B, Koplay M, Ozturk E et-al. Retroaortic left renal vein: multidetector computed tomography angiography findings and its clinical importance. Acta Radiol. 2007;48 (3): 355-60. doi:10.1080/02841850701244755 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Bass JE, Redwine MD, Kramer LA et-al. Spectrum of congenital anomalies of the inferior vena cava: cross-sectional imaging findings. Radiographics. 20 (3): 639-52. Radiographics (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 4. Anjamrooz SH, Azari H, Abedinzadeh M. Abnormal patterns of the renal veins. (2012) Anatomy & cell biology. 45 (1): 57-61. doi:10.5115/acb.2012.45.1.57 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Renal vein varices
- Retroaortic left renal vein
- Posterior nutcracker syndrome
- Circumaortic left renal vein
- Caval variants
- Duplication of the inferior vena cava
- Nutcracker syndrome
- Reporting tips for aortic aneurysms
- Pelvic congestion syndrome
- Developmental anomalies of the kidney and ureter
- Renal vein anomalies
- Double retroaortic left renal vein
- Beaver tail liver
- Retroaortic left renal vein - type 4
- Circumcaval ureter
- Circumaortic left renal vein
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Castleman disease
- Calyceal diverticulum
- Giant hepatic hemangioma
- Retroaortic left renal vein - type II
- Retroaortic left renal vein - type I
- Type IV left renal vein
- Undifferentiated carcinoma of the pancreas
- Traumatic renal injury - AAST grade IV injury
- Circumaortic left renal vein
- Multitrauma
- Colonic diverticulitis progress to diverticular abscess
- Hydronephrosis due to ureteric calculus
- Superior mesenteric artery syndrome
- Petersen hernia
- Retroaortic left renal vein
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera[+][+]
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries[+][+]
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system[+][+]
- veins
- anastomoses[+][+]
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries[+][+]
- lymphatics[+][+]
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses