A rim rent tear of the rotator cuff, also known as partial articular surface tendon avulsion, is a specific subtype of partial-thickness rotator cuff tear that involves the articular surface footprint at the site of tendon attachment into the greater tubercle of the humerus 2.
Such small tears can extend along the tendon fibres, causing tendon delamination, which corresponds to Snyder III or IV classification. This sort of tear is relatively common and also can involve the infraspinatus tendon 3. Involvement of the bursal surface can also occur (reverse partial articular surface tendon avulsion).
On this page:
Epidemiology
Partial articular surface tendon avulsion lesions are frequent in overhead athletes, younger people and smokers.
Pathology
-
intrinsic factors
ageing with changes in rotator cuff vascularity and metabolic changes associated
-
extrinsic factors
shear stresses on the supraspinatus tendon from narrowing of the coracoacromial arch (extrinsic impingement)
microtrauma from repetitive contact of the articular surface of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons with the posterosuperior part of the glenoid during arm abduction and lateral rotation
Clinical presentation
Not all partial articular surface tendon avulsion lesions are symptomatic. Often shoulder pain when lifting outwards, overhead and throwing.
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
An x-ray of the shoulder with an anteroposterior view, axillary lateral view and a supraspinatus outlet view are not specific.
Ultrasound
It may be seen as an echogenic edge and a cortical defect at the footprint. However anisotropy artifacts often make it challenging to recognise partial articular supraspinatus tendon avulsion by ultrasound.
MRI
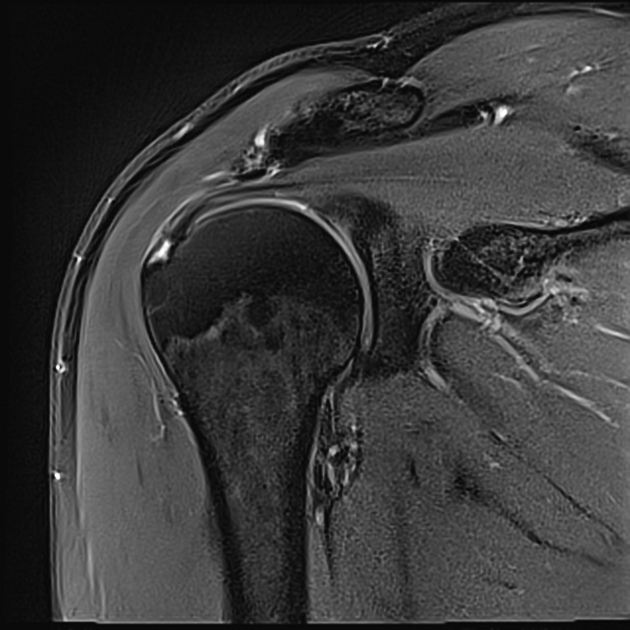
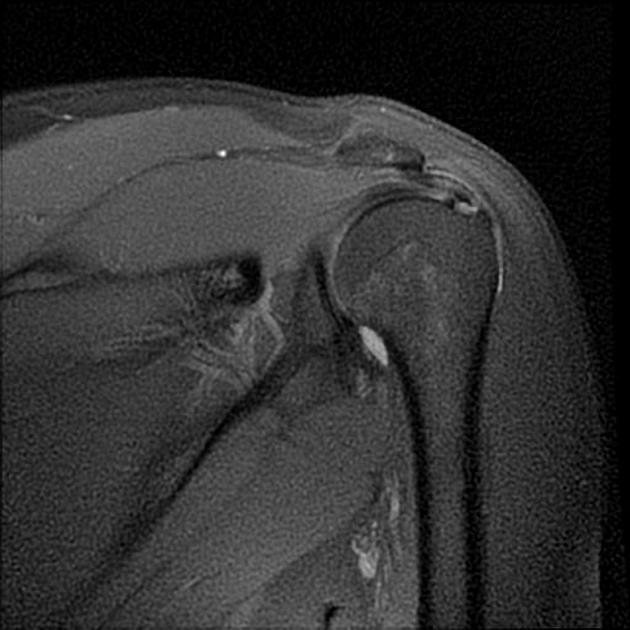
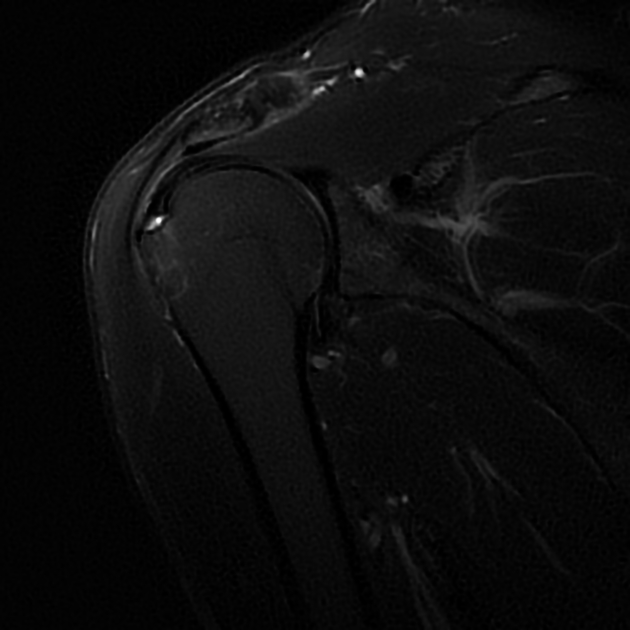
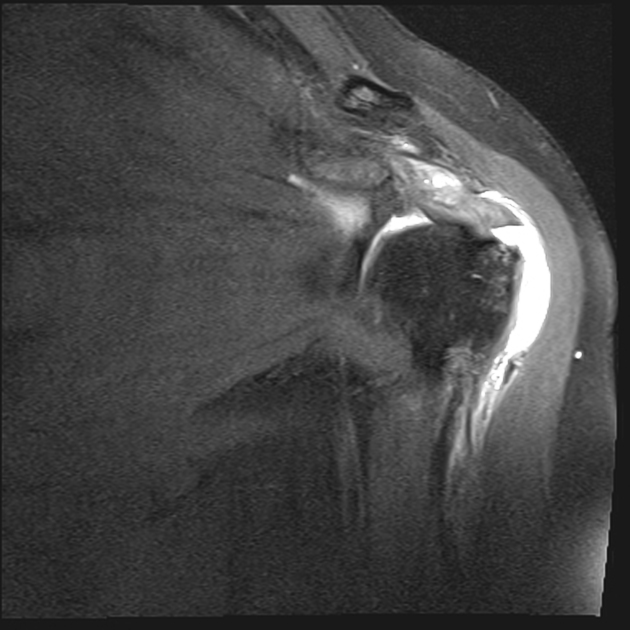
Partial articular surface tendon avulsion lesions appear in coronal T2 images and in glenohumeral arthrography as linear fluid signal defects at the articular surface of the supraspinatus tendon, near the attachment (footprint) on bone interface.
Treatment and prognosis
Initially conservative treatment with activity modification, without overhead or pain-provoking actions, and physical therapy.
Surgery if the pain is not coming down by three to six months of nonoperative treatment and than one half of the thickness of the supraspinatus tendon is torn.
Surgical options
arthroscopic debridement of the tear
debridement with acromioplasty
rotator cuff repair with or without acromioplasty
History and etymology
The term “rim-rent” was first used by the American surgeon Ernest Amory Codman (1869-1940) 9 in 1934. Of interest, is that Codman was the first skiagrapher (radiologist) appointed at the Boston Children's Hospital in 1899 3,4,9.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.