Sacral insufficiency fracture
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Ayush Goel had no recorded disclosures.
View Ayush Goel's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Wilson Tao had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Wilson Tao's current disclosures- Sacral insufficiency fractures
- Insufficiency fractures of the sacrum
Sacral insufficiency fractures are a subtype of stress fractures, which are the result of normal stresses on abnormal bone, most frequently seen in the setting of osteoporosis. They fall under the broader group of pelvic insufficiency fractures.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Risk factors
Risk factors are those of osteoporosis as well as other abnormal bone conditions, including 6:
osteoporosis: most common
Associations
Long-term bisphosphonate use has been associated with insufficiency fractures.
Clinical presentation
They are usually seen in elderly females who present with low back pain without any history of significant trauma.
Pathology
They are most frequently seen in the setting of osteoporosis, although any process which weakens bone is a risk factor.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
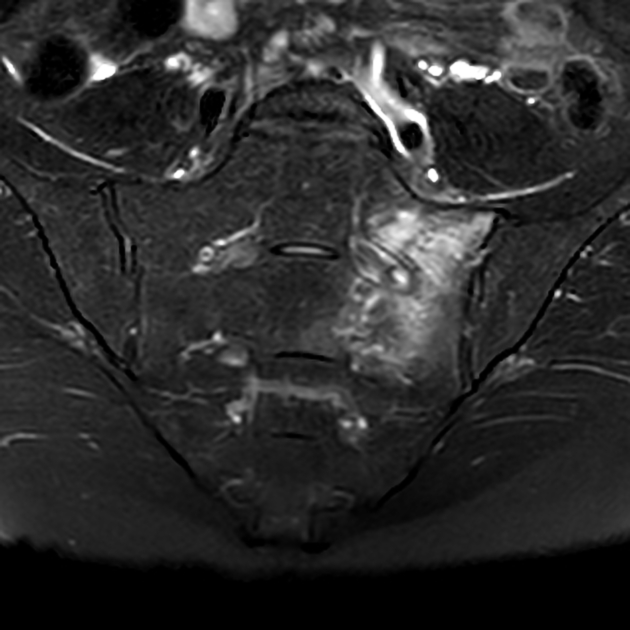
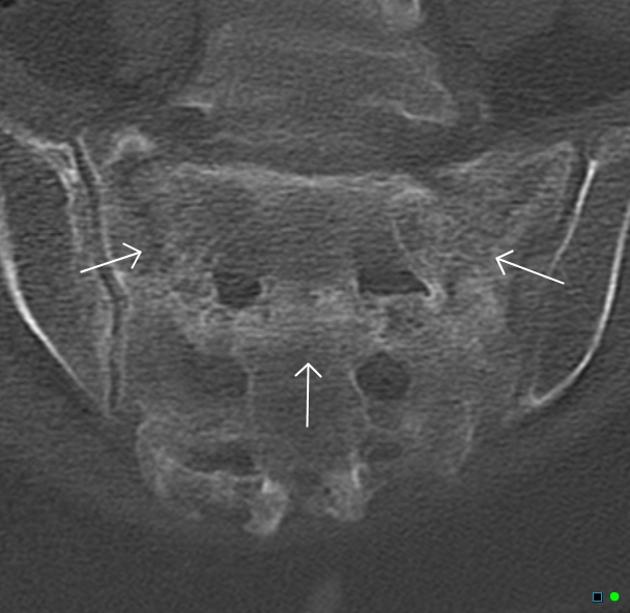
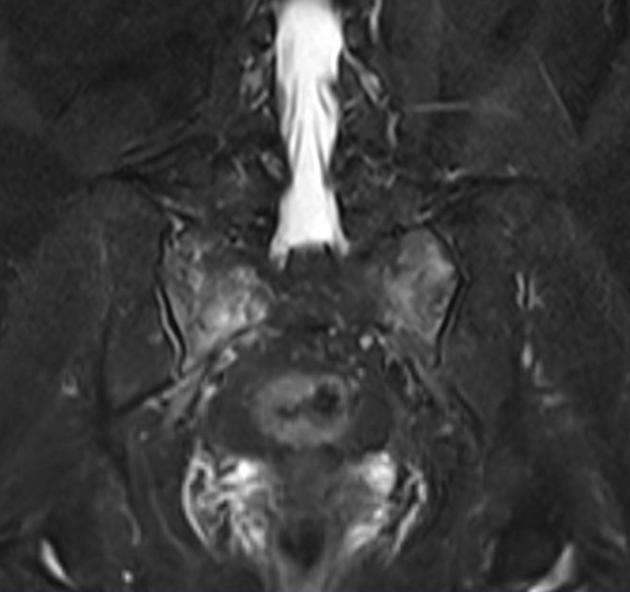
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
They may be normal, or a sclerotic line may be noted in the involved region(s).
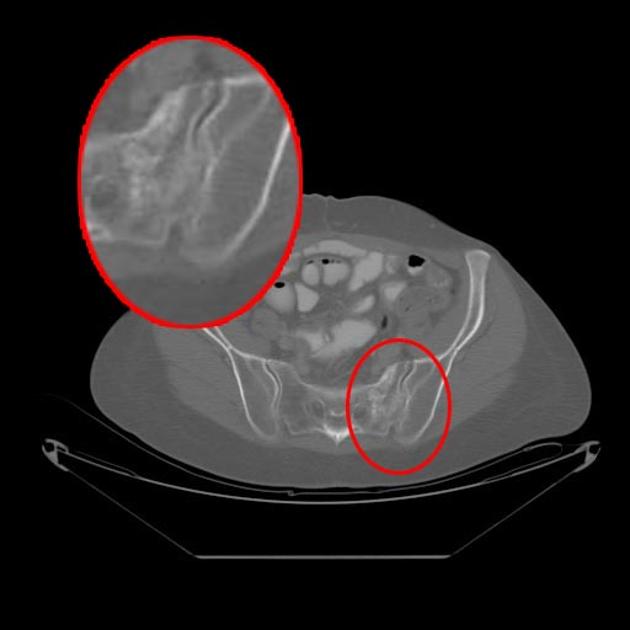
CT
May show a fracture line along with sclerosis that is parallel to the sacroiliac joint, although even CT imaging is less sensitive as compared to MRI and nuclear imaging.
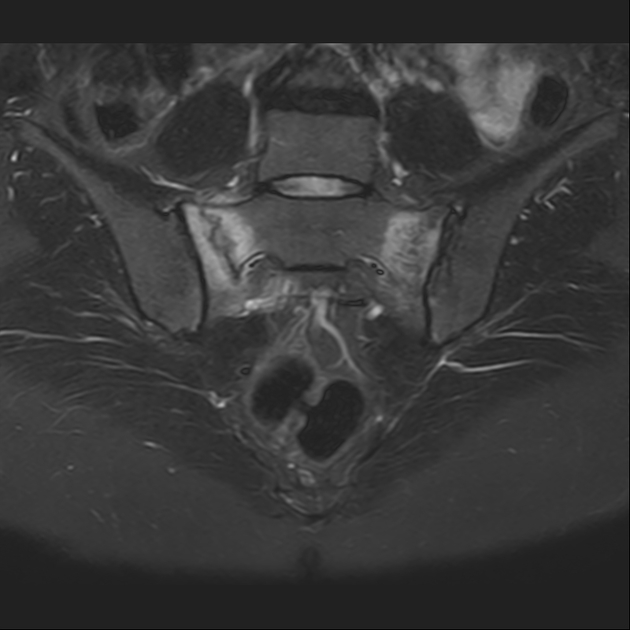
MRI
Can depict bone marrow oedema as early as 18 days after the development of symptoms.
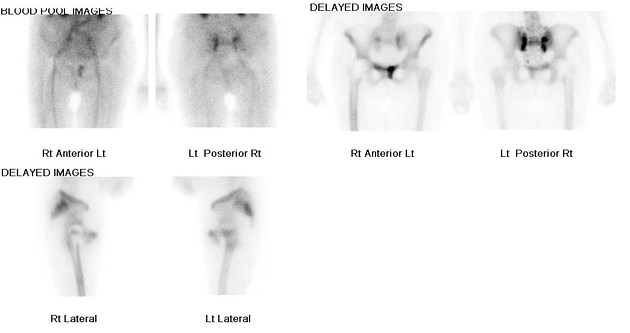
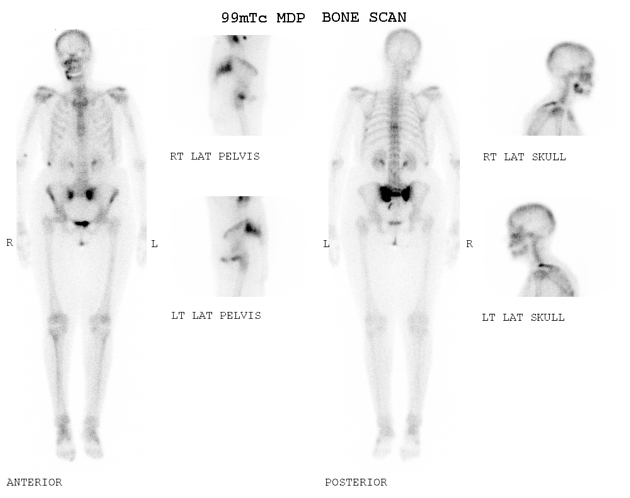
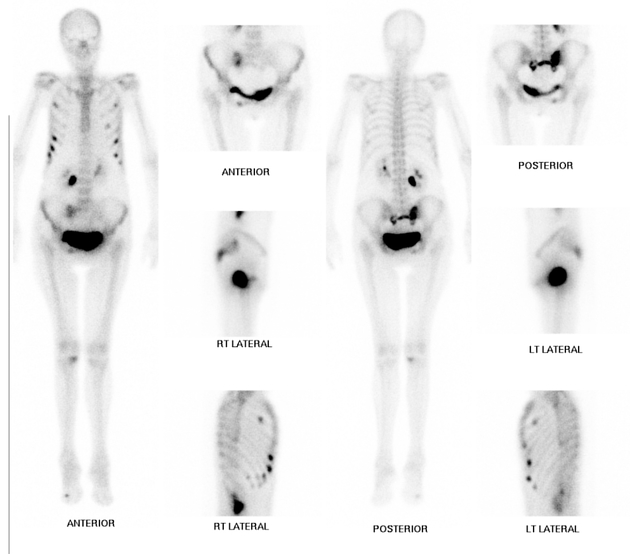
Nuclear medicine
Uptake of Tc-99m MDP is also sensitive but not specific. A typical H-sign or Honda sign (uptake in H pattern) may be noted in 20-40% of cases and is considered diagnostic.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment options can be variable ranging from conservative management to sacroplasty 5.
References
- 1. Lee Y, Bong H, Kim J, Chung D. Sacral Insufficiency Fracture, Usually Overlooked Cause of Lumbosacral Pain. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008;44(3):166-9. doi:10.3340/jkns.2008.44.3.166 - Pubmed
- 2. Longhino V, Bonora C, Sansone V. The management of sacral stress fractures: current concepts. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2012;8 (3): 19-23. Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 3. Lyders EM, Whitlow CT, Baker MD et-al. Imaging and treatment of sacral insufficiency fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31 (2): 201-10. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1666 - Pubmed citation
- 4. Fujii M, Abe K, Hayashi K et al. Honda Sign and Variants in Patients Suspected of Having a Sacral Insufficiency Fracture. Clin Nucl Med. 2005;30(3):165-9. doi:10.1097/00003072-200503000-00004 - Pubmed
- 5. Butler C, Given C, Michel S, Tibbs P. Percutaneous Sacroplasty for the Treatment of Sacral Insufficiency Fractures. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184(6):1956-9. doi:10.2214/ajr.184.6.01841956
- 6. Yoder K, Bartsokas J, Averell K, McBride E, Long C, Cook C. Risk Factors Associated with Sacral Stress Fractures: A Systematic Review. J Man Manip Ther. 2015;23(2):84-92. doi:10.1179/2042618613Y.0000000055 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Sacral insufficiency fracture
- Sacral insufficiency fracture
- Sacral insufficiency fracture
- Sacral insufficiency fracture
- Sacral insufficiency fracture
- Sacral insufficiency fractures
- Sacral and parasymphyseal insufficiency fractures
- Honda sign
- Honda sign
- Honda sign
- Sacral insufficiency fractures
- Sacral insufficiency fracture
- Sacral insufficiency fracture
Related articles: Fractures
-
fracture
- terminology
- fracture location
- diaphyseal fracture
- metaphyseal fracture
- physeal fracture
- epiphyseal fracture
- fracture types
- avulsion fracture
- articular surface injuries
- complete fracture
- incomplete fracture
- infraction
- compound fracture
- pathological fracture
- stress fracture
- fracture displacement
- fracture location
- fracture healing
- skull fractures
-
facial fractures
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
- alveolar process fractures
- frontal sinus fracture
- isolated zygomatic arch fractures
- mandibular fracture
- nasal bone fracture
- orbital blow-out fracture
- paranasal sinus fractures
- complex fractures
- dental fractures
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
-
spinal fractures
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- AO classification of upper cervical injuries
- AO classification of subaxial injuries
- Anderson and D'Alonzo classification (odontoid fracture)
- Roy-Camille classification (odontoid process fracture)
- Gehweiler classifcation (atlas fractures)
- Levine and Edwards classification (hangman fracture)
- Allen and Ferguson classification (subaxial spine injuries)
- subaxial cervical spine injury classification (SLIC)
- thoracolumbar spinal fracture classification systems
- three column concept of spinal fractures (Denis classification)
- classification of sacral fractures
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- spinal fractures by region
- spinal fracture types
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
- rib fractures
- sternal fractures
-
upper limb fractures
- classification
- Rockwood classification (acromioclavicular joint injury)
- AO classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO/OTA classification of distal humeral fractures
- Milch classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Weiss classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Bado classification of Monteggia fracture-dislocations (radius-ulna)
- Mason classification (radial head fracture)
- Frykman classification (distal radial fracture)
- Mayo classification (scaphoid fracture)
- Hintermann classification (gamekeeper's thumb)
- Eaton classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- Keifhaber-Stern classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- upper limb fractures by region
- shoulder
- clavicular fracture
-
scapular fracture
- acromion fracture
- coracoid process fracture
- glenoid fracture
- humeral head fracture
- proximal humeral fracture
- humeral neck fracture
- arm
- elbow
- forearm
- wrist
-
carpal bones
- scaphoid fracture
- lunate fracture
- capitate fracture
- triquetral fracture
- pisiform fracture
- hamate fracture
- trapezoid fracture
- trapezium fracture
- hand
- shoulder
- classification
- lower limb fractures
- classification by region
- pelvic fractures
- hip fractures
- Pipkin classification (femoral head fracture)
- Garden classification (hip fracture)
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Cooke and Newman classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Johansson classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Vancouver classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- femoral
- knee
- Schatzker classification (tibial plateau fracture)
- AO classification of distal femur fractures
- Meyers and McKeevers classification (anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture)
- tibia/fibula
- Watson-Jones classification (tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture)
- ankle
- foot
- Berndt and Harty classification (osteochondral lesions of the talus)
- Sanders CT classification (calcaneal fracture)
- Hawkins classification (talar neck fracture)
- Myerson classification (Lisfranc injury)
- Nunley-Vertullo classification (Lisfranc injury)
- pelvis and lower limb fractures by region
- pelvic fracture
- sacral fracture
- coccygeal fracture
-
hip
- acetabular fracture
- femoral head fracture
-
femoral neck fracture
- subcapital fracture
- transcervical fracture
- basicervical fracture
-
trochanteric fracture
- pertrochanteric fracture
- intertrochanteric fracture
- subtrochanteric fracture
- femur
- mid-shaft fracture
- bisphosphonate-related fracture
- distal femoral fracture
- knee
- avulsion fractures
- Segond fracture
- reverse Segond fracture
- anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- arcuate complex avulsion fracture (arcuate sign)
- biceps femoris avulsion fracture
- iliotibial band avulsion fracture
- semimembranosus tendon avulsion fracture
- Stieda fracture (MCL avulsion fracture)
- patellar fracture
- tibial plateau fracture
- avulsion fractures
- leg
- tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture
- tibial shaft fracture
- fibular shaft fracture
- Maisonneuve fracture
- ankle
- foot
- tarsal bones
- metatarsal bones
- phalanges
- classification by region
- terminology




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.