Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) refers to deafness secondary to conditions affecting the inner ear, internal acoustic canal, cerebellopontine angle, or vestibulocochlear nerve.
It an be classified audiometrically into two types
- sensory (cochlear)
- neural (retrocochlear)
Pathology
Conditions that cause sensorineural hearing loss can be divided by location:
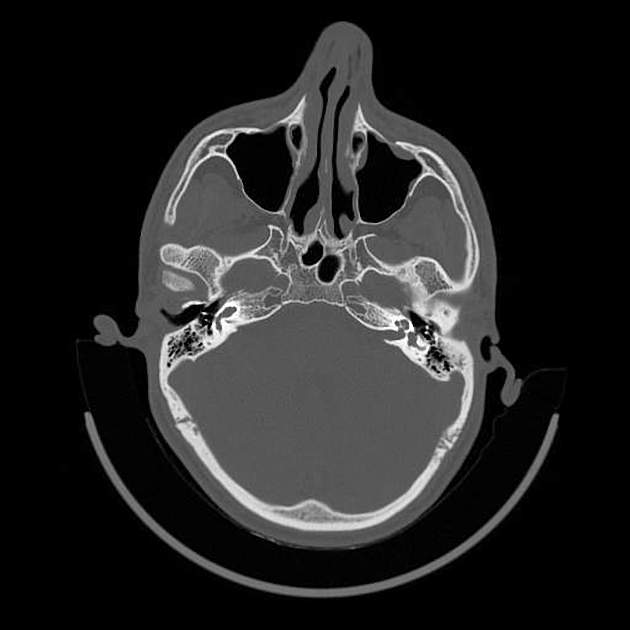
- inner ear
-
bony labyrinth
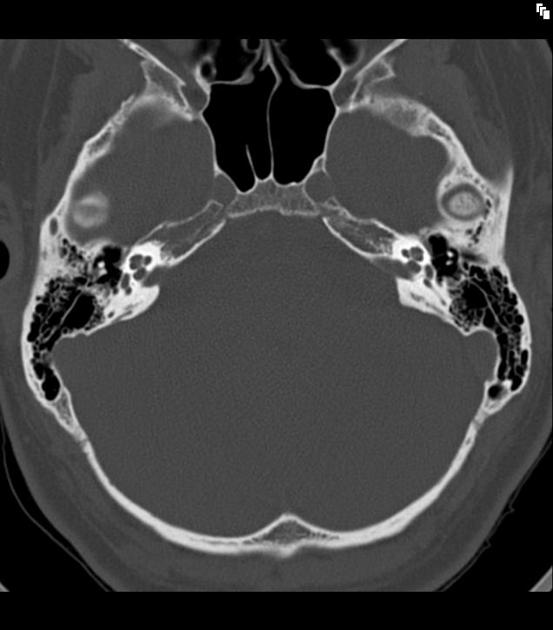
- otosclerosis (and other causes of otic capsule demineralisation)
- trauma, e.g. temporal bone fracture
- congenital (developmental or acquired)
-
membranous labyrinth
- infectious, e.g. labyrinthitis
- can be complicated labyrinthine ossificans
- trauma, e.g. intracochlear haemorrhage
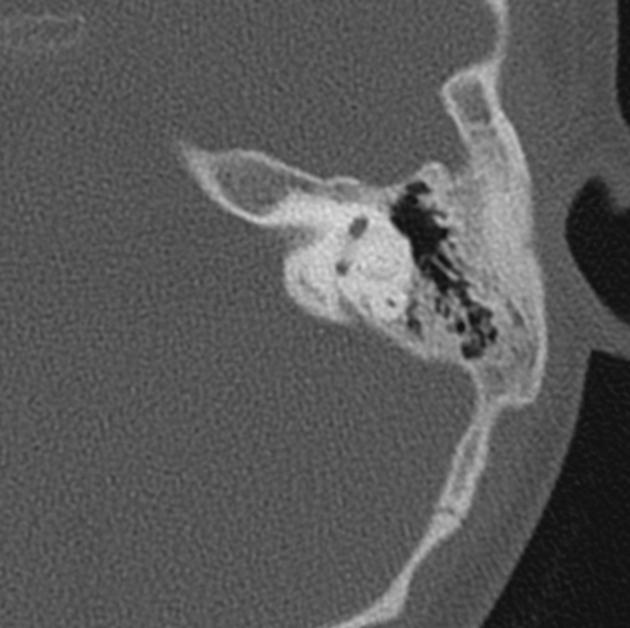
- intracochlear schwannoma
- Meniere disease
- infectious, e.g. labyrinthitis
-
bony labyrinth
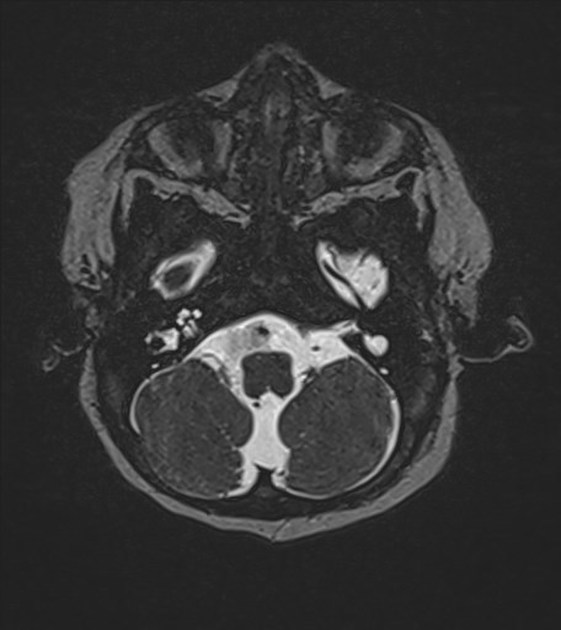
- internal acoustic canal or cerebellopontine angle mass or vestibulocochlear nerve
- vestibular schwannoma
- meningioma
- vascular (rare), e.g. haemangiomas
- metastases: most commonly lung, breast, melanoma, lymphoma
- cystic lesions, e.g. epidermoid cyst, arachnoid cyst
- cochlear nerve anomalies
- superficial siderosis




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.