Spermatic cord liposarcoma
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Michael P. Hartung had no recorded disclosures.
View Michael P. Hartung's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Andrea Molinari had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Andrea Molinari's current disclosures- Spermatic cord liposarcomas
Spermatic cord liposarcomas are the most common malignant tumour of the spermatic cord. Most present as painless, slow-growing masses and can be mistaken for inguinal hernias. They are usually well-differentiated and spread by local extension.
On this page:
Epidemiology
In a large population-based registry, the annual incidence of spermatic cord tumour (SCT) is 0.3 cases/million 3.
Clinical presentation
Most present as painless, slow-growing masses. They can be mistaken for an inguinal hernia, hydrocele, or other paratesticular tumours.
Pathology
Most are low-grade and well-differentiated and spread by local extension. High-grade tumours can spread via haematogenous or lymphatic routes 3.
In a large population-based registry, 362 patients with SCT were identified, with histological subtypes of liposarcoma (46%), leiomyosarcoma (20%), histiocytoma (13%), and rhabdomyosarcoma (9%) 3.
Radiographic features
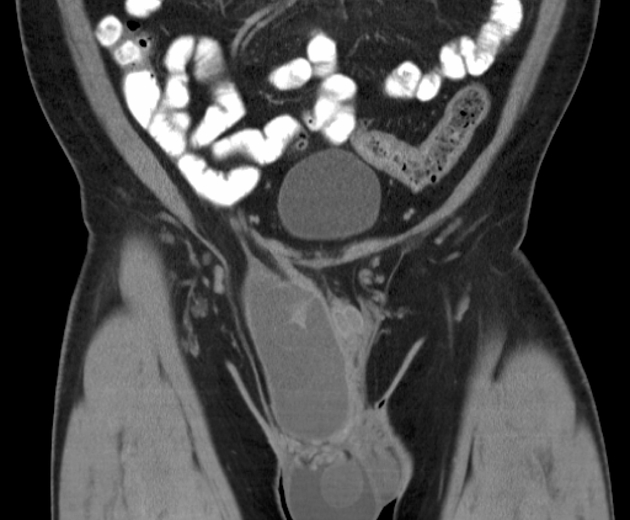
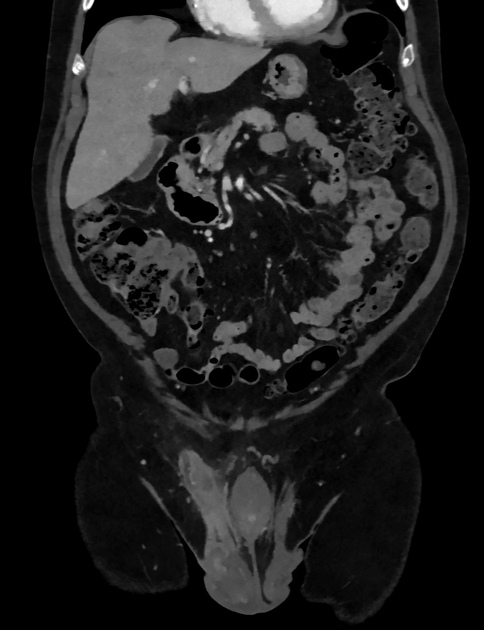
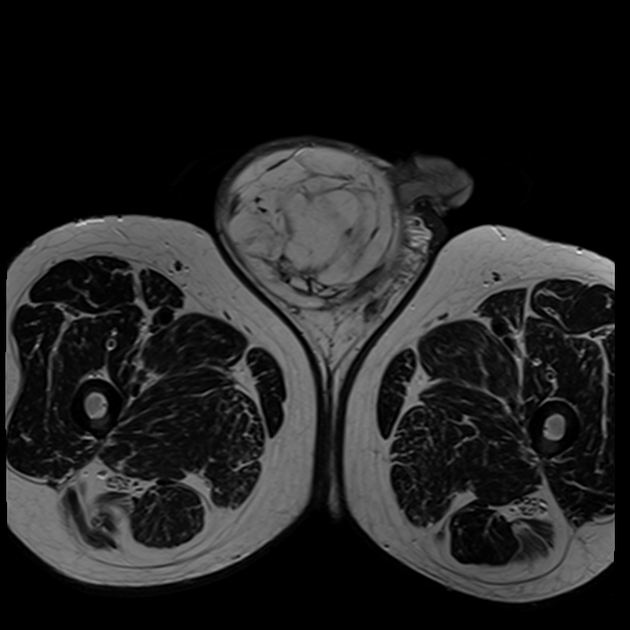
CT and MRI provide greater characterisation and staging information than ultrasound. They appear as a fat-containing tumour with variable amounts of soft tissue, nodularity, and septations.
Treatment and prognosis
Standard surgical treatment includes high orchidectomy and resection of the tumour and spermatic cord. Lymph node dissection is occasionally performed. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy depend on the tumour grade, stage, and risk of recurrence1.
Differential diagnosis
Lipoma is the most common benign tumour of the spermatic cord, and much more common than liposarcoma (45% of paratesticular masses)3. Other malignant tumours of the spermatic cord include leiomyosarcoma, histiocytoma, and rhabdomyosarcoma.
See also
References
- 1. Yamamichi G, Nakata W, Yamamoto A, Tsujimura G, Tsujimoto Y, Nin M, Tsujihata M. Liposarcoma of the spermatic cord associated with scrotum lipoma: A case report and review of the literature. (2018) Urology case reports. 17: 114-116. doi:10.1016/j.eucr.2018.01.022 - Pubmed
- 2. Rodríguez D, Barrisford GW, Sanchez A et-al. Primary spermatic cord tumors: disease characteristics, prognostic factors, and treatment outcomes. Urol. Oncol. 2014;32 (1): 52.e19-25. doi:10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.08.009 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Akbar SA, Sayyed TA, Jafri SZ, Hasteh F, Neill JS. Multimodality imaging of paratesticular neoplasms and their rare mimics. (2003) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 23 (6): 1461-76. doi:10.1148/rg.236025174 - Pubmed
- 4. Woodward PJ, Schwab CM, Sesterhenn IA. From the archives of the AFIP: extratesticular scrotal masses: radiologic-pathologic correlation. (2003) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 23 (1): 215-40. doi:10.1148/rg.231025133 - Pubmed
- 5. Li F, Tian R, Yin C, Dai X, Wang H, Xu N, Guo K. Liposarcoma of the spermatic cord mimicking a left inguinal hernia: a case report and literature review. (2013) World journal of surgical oncology. 11: 18. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-11-18 - Pubmed
- 6. Chalouhy C, Ruck JM, Moukarzel M, Jourdi R, Dagher N, Philosophe B. Current management of liposarcoma of the spermatic cord: A case report and review of the literature. (2017) Molecular and clinical oncology. 6 (3): 438-440. doi:10.3892/mco.2017.1157 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.