Splenogonadal fusion
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Matt A. Morgan had no recorded disclosures.
View Matt A. Morgan's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yaïr Glick had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yaïr Glick's current disclosuresSplenogonadal fusion is a rare anomaly that occurs when there is congenital fusion between a portion of the spleen and a gonad or other mesonephric derivative.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Much more common in male patients (~95%), occurs most commonly on the left (98%) and usually involves the testis (95%). Has been found in patients from birth to 81 years old 3.
Clinical presentation
Most often an incidental finding but may present as a left-sided testicular mass or may present as cryptorchidism. The continuous type (see Pathology below) may be associated with other congenital anomalies, such as limb deformities or micrognathia.
Pathology
The fusion of the two tissue types is assumed to occur between the 4th-10th week of gestation.
There are two main types:
continuous: gonad linked to spleen by a trans- or retroperitoneal cord of splenic tissue or fibrous cord with nodules of splenic tissue; often associated with other congenital anomalies
discontinuous: ectopic rests of splenic tissue are present in the gonad
Splenogonadal fusion with the ductus deferens or spermatic cord is exceedingly rare.
Radiographic features
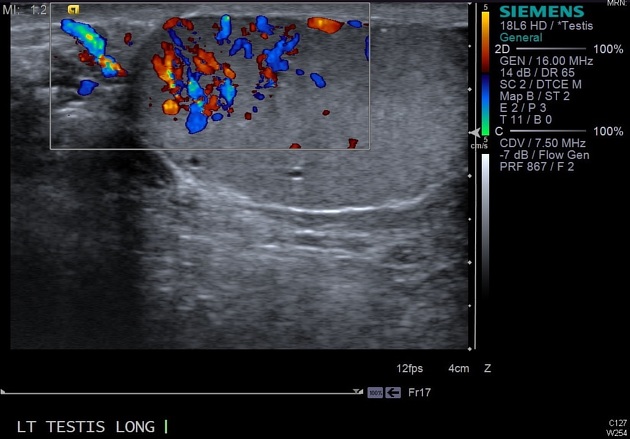
Ultrasound
the discontinuous form appears as a homogeneous, iso- to hypoechoic mass in the testis and is indistinguishable from a testicular malignancy
colour Doppler may show a central feeding vessel that branches out toward the rest of the splenic tissue
MRI
may show continuous or discontinuous relation between ectopic splenic tissue and gonad
Nuclear medicine
if suspected prospectively, Tc99m-sulfur colloid may be used to identify ectopic splenic tissue in a gonad
Treatment and prognosis
Splenogonadal fusion is thought to have a benign prognosis, but is rarely diagnosed before orchidectomy.
Differential diagnosis
References
- 1. Bhatt S, Rubens DJ, Dogra VS. Sonography of benign intrascrotal lesions. Ultrasound Q. 2006;22 (2): 121-36. Pubmed citation
- 2. Stewart VR, Sellars ME, Somers S et-al. Splenogonadal fusion: B-mode and color Doppler sonographic appearances. J Ultrasound Med. 2005;23 (8): 1087-90. Pubmed citation
- 3. Ando S, Shimazui T, Hattori K et-al. Splenogonadal fusion: case report and review of published works. Int. J. Urol. 2006;13 (12): 1539-41. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2006.01598.x - Pubmed citation
- 4. Vikram S. Dogra, Gregory T. MacLennan. Genitourinary Radiology: Male Genital Tract, Adrenal and Retroperitoneum. ISBN: 9781447148999
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- coeliac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses
Related articles: Splenic pathology
- normal appearance of the spleen
- pseudolesion of the spleen: inhomogeneous splenic enhancement
-
splenic lesions and anomalies
- congenital anomalies
- mass lesions
- benign
- indeterminate
- malignant
- infiltrative processes
- miscellaneous
- incidental splenic lesion (approach)
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta praevia
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynaecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumours
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumours of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumours
- mixed germ cell tumour
- yolk sac tumour (endodermal sinus tumour)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumour
- sex cord / stromal tumours of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumour of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumours (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumours
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.