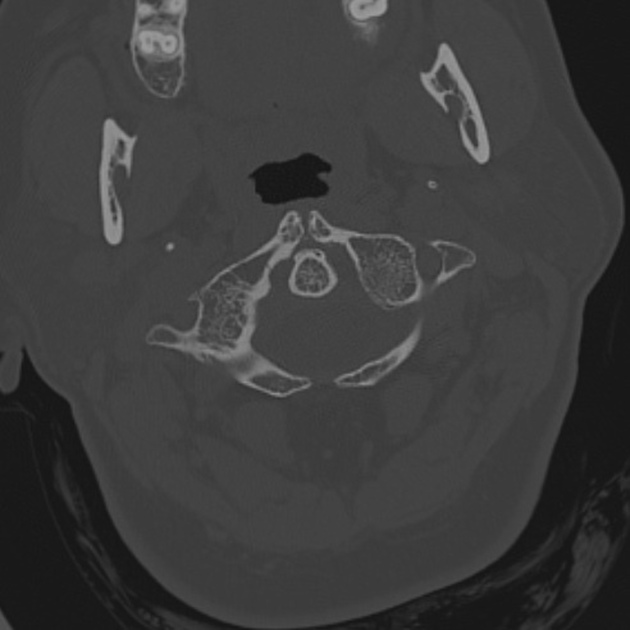
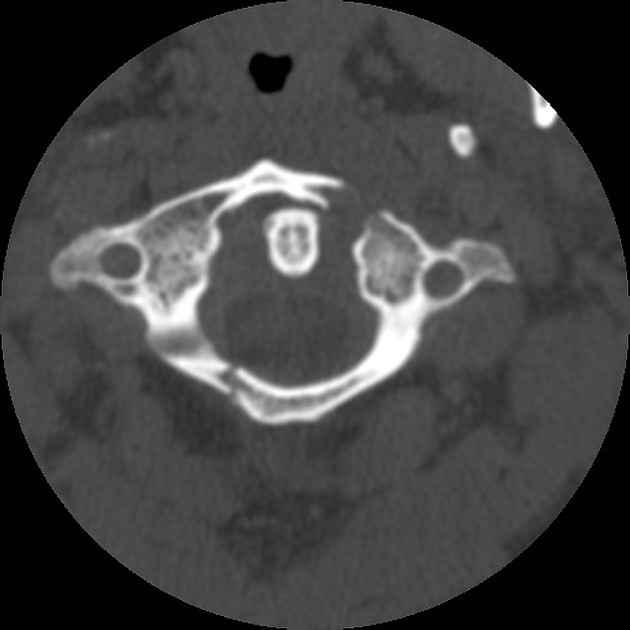
Split atlas
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- bipartite atlas
Split or bipartite atlas is the rare congenital anomaly where the atlas is split into two halves by fusion defects in both the anterior and posterior arches. The osseous defects are spanned by fibrous tissue.
They are usually asymptomatic and found incidentally on spinal imaging. Patients may have neck pain and rarely develop cervical myelopathy.
The anterior arch defect is mostly in the midline and usually smaller than the posterior arch defect, which is almost always in the midline.
Care should be taken to avoid misdiagnosing a Jefferson fracture, noting that fusion defects will have broad or tapered osseous margins that are rounded and well-corticated.
References
- 1. Frick BS, Figiel JH, Rominger M. ["Split atlas" - a rare congenital malformation of the anterior and posterior atlantic arc]. (2007) RoFo : Fortschritte auf dem Gebiete der Rontgenstrahlen und der Nuklearmedizin. 179 (8): 855-6. doi:10.1055/s-2006-927343 - Pubmed
- 2. Ramdhan, RC, et al. The Split Atlas Anomaly: A Comprehensive Review (2017) Spine Scholar 1:37-44.
- 3. Bonneville F, Jacamon M, Runge M, Jacquet G, Bonneville JF. Split atlas in a patient with odontoid fracture. (2004) Neuroradiology. 46 (6): 450-2. doi:10.1007/s00234-004-1189-z - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Spine
-
osteology
- vertebrae
- spinal canal
- cervical spine
- thoracic spine
- lumbar spine
- sacrum
- coccyx
-
anatomical variants
- vertebral body
- neural arch
- transitional vertebrae
- ossicles
- ossification centres
- intervertebral disc
- articulations
- ligaments
- musculature of the vertebral column
- muscles of the neck
- muscles of the back
-
suboccipital muscle group
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- splenius capitis muscle
- splenius cervicis muscle
- erector spinae group
- transversospinalis group
- quadratus lumborum muscle
-
suboccipital muscle group
- spinal meninges and spaces
-
spinal cord
- gross anatomy
-
white matter tracts (white matter)
- corticospinal tract
- anterolateral columns
- lateral columns
-
dorsal columns
- fasiculus gracilis (column of Goll)
- fasiculus cuneatus (column of Burdach)
- grey matter
- nerve root
- central canal
- functional anatomy
- spinal cord blood supply
- sympathetic chain





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.