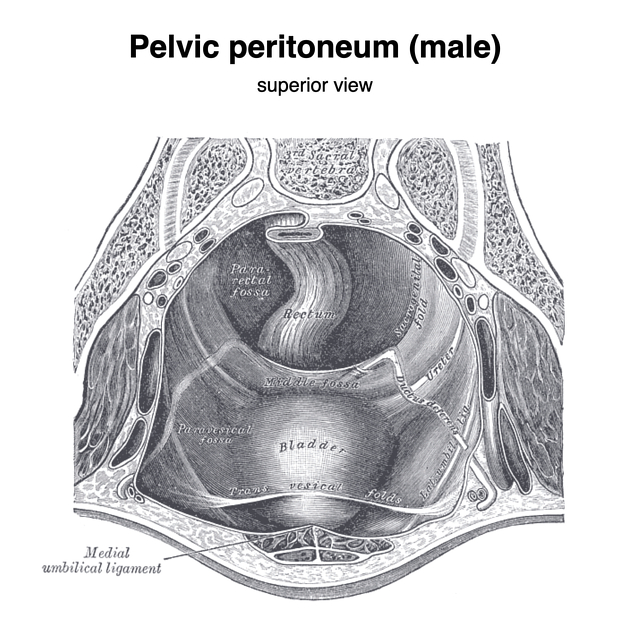
Supravesical fossa
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Juliana K. Yee had no recorded disclosures.
View Juliana K. Yee's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Supravesical fossae
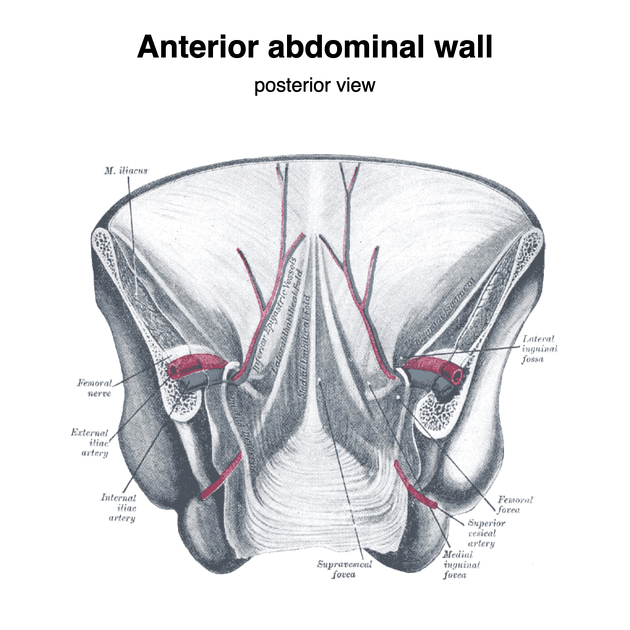
The supravesical fossae are concave depressions of peritoneum in the paravesical space bounded by the median umbilical fold and the medial umbilical folds. It partially overlies the inguinal (Hesselbach’s) triangle. The supravesical fossae are usually occupied by small bowel loops and the urinary bladder fundus when the bladder is distended.
Related pathology
Supravesical hernias arise from this fossa. If the hernia continues through the abdominal wall this is classed as a direct inguinal hernia. If the hernia remains in the abdomen, passing into spaces around the urinary bladder it is classed as an internal supravesical hernia.
History and etymology
The term supravesical fossa was introduced by Waldeyer in 1874 4.
References
- 1. Howard FM, Perry P, Carter J et-al. Pelvic Pain. LWW. (2000) ISBN:0781717248. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Yeo CJ, McFadden DW, Pemberton JH et-al. Shackelford's Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. Elsevier Health Sciences. (2012) ISBN:1455738077. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Schultess G, Zollikofer C. Diseases of the Abdomen and Pelvis. Springer Science & Business Media. (2012) ISBN:8847021413. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Sozen I, Sozen NJ, Sozen. Inguinal mass due to an external supravesical hernia and acute abdomen due to an internal supravesical hernia: a case report and review of the literature. (2004) Hernia : the journal of hernias and abdominal wall surgery. doi:10.1007/s10029-004-0222-9 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- coeliac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.