Tolosa-Hunt syndrome is an idiopathic inflammatory condition that involves the cavernous sinus and orbital apex and is essentially a clinical diagnosis of exclusion.
On this page:
Epidemiology
The estimated incidence of Tolosa-Hunt syndrome is 1 per 1,000,000 person-years with an average age of onset at 41 years 14.
Associations
Clinical presentation
Clinically it refers to the presence of a painful ophthalmoplegia secondary to surrounding cavernous sinus inflammation. Tolosa-Hunt syndrome is essentially a clinical diagnosis of exclusion.
Pathology
The constant pain that characterises the disorder is believed to be due to compression resulting from fibroblast proliferation and infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells, along with thickening of dura mater within the cavernous sinus 15. Occasional granulomas and giant cells have been reported 15.
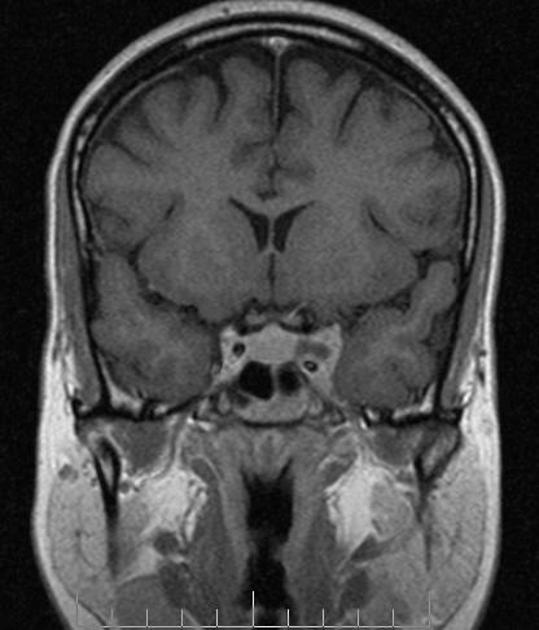
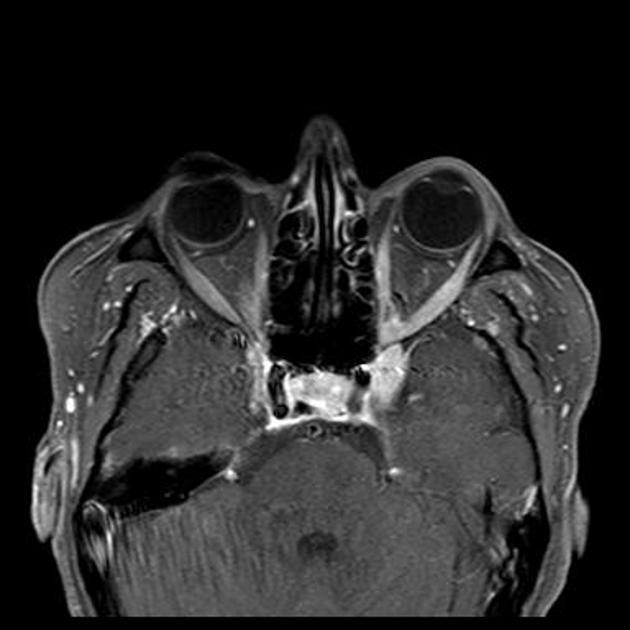
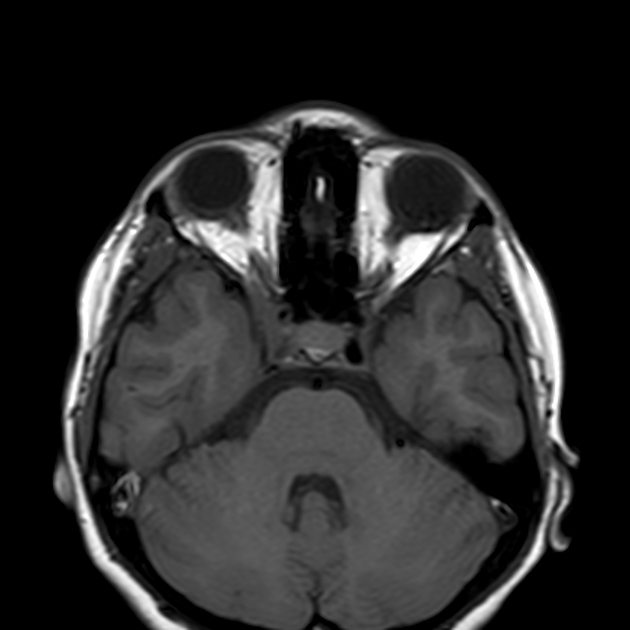
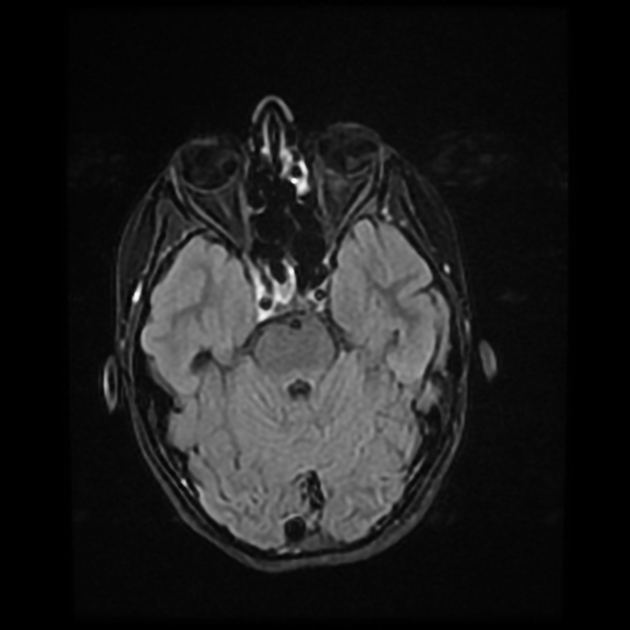
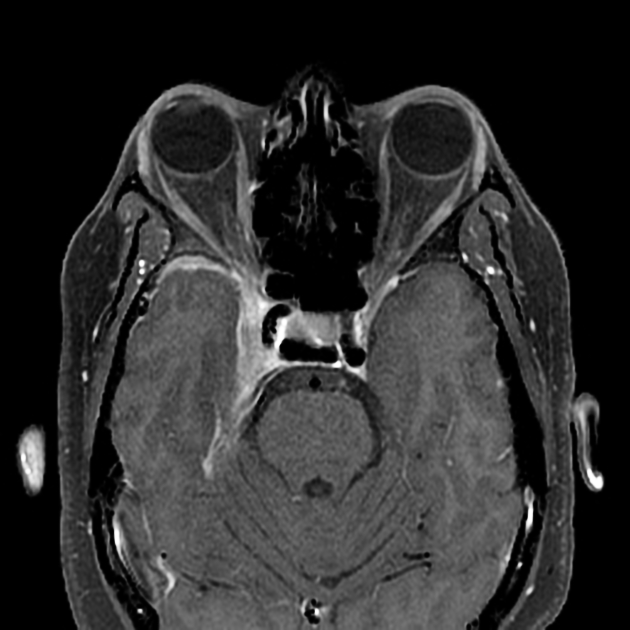
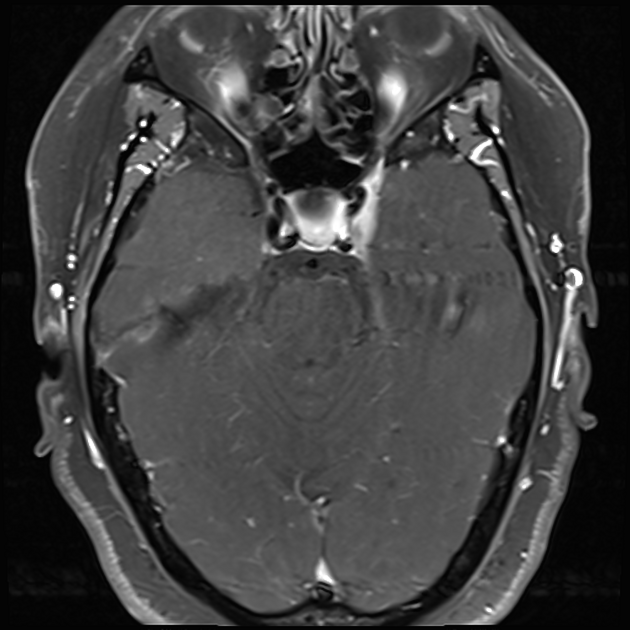
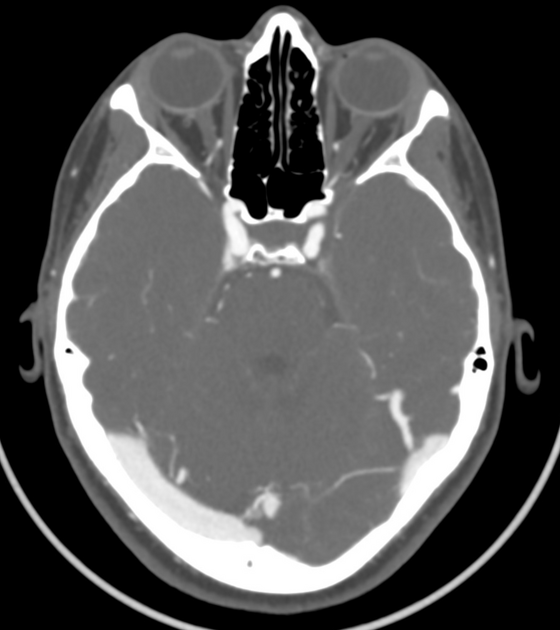
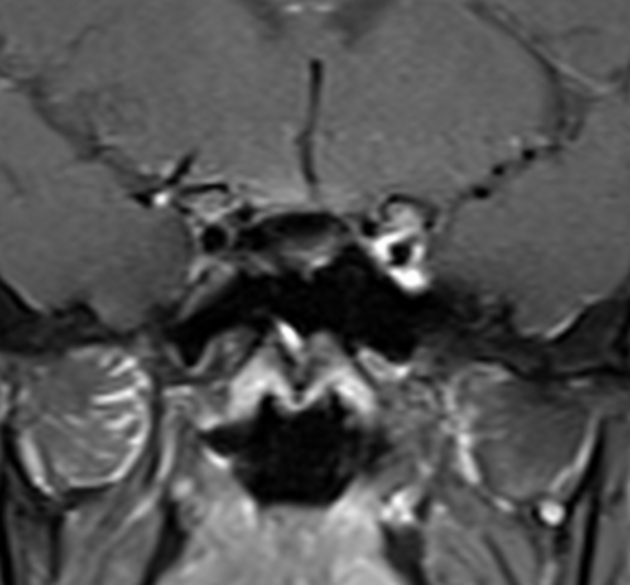
Radiographic features
CT
May show asymmetrical enlargement in the region of the cavernous sinus on the affected side +/- contrast enhancement 1.
The secondary criteria are internal carotid artery narrowing, extension towards the superior orbital fissure and orbital apex.
MRI
May show evidence of inflammatory changes in the region of the anterior cavernous sinus, superior orbital fissure +/- orbital apex. Signal characteristics are non-specific 10 (clinical scenario essential to diagnosis) but may include:
T1: involved region is isointense 2 to hyperintense 8 compared with muscle
T2: involved area is hyperintense
T1 C+ (Gd): may show contrast enhancement during active phase with resolution of enhancement following treatment 5,9
Treatment and prognosis
The condition is often successfully amenable to steroid treatment and does not usually require biopsy unless there is concern that it represents malignancy 15.
History and etymology
It was initially described by Eduardo Tolosa Colomer (1900-1981) 12, a Spanish neurosurgeon, in 1954 3 (note his son is a pioneering neurologist with a similar name: Eduardo Tolosa Sarró (fl. 2019)) and then by the American neurosurgeon William Edward Hunt (1921-1999) et al. in 1961 4,12. The disease is also known as painful opthalmoplegia.
Differential diagnosis
Consider other pathological processes presenting with similar clinical features such as meningioma, sarcoidosis, pituitary tumours, tuberculous meningitis, lymphoma, cavernous sinus thrombosis 13.





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.