Trochlear nerve
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- Trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- Trochlear nerve (IV)
- Fourth cranial nerve
- Cranial nerve 4
- Cranial nerve IV
- CN IV
- Nervus trochlearis
- Nervus cranialis IV
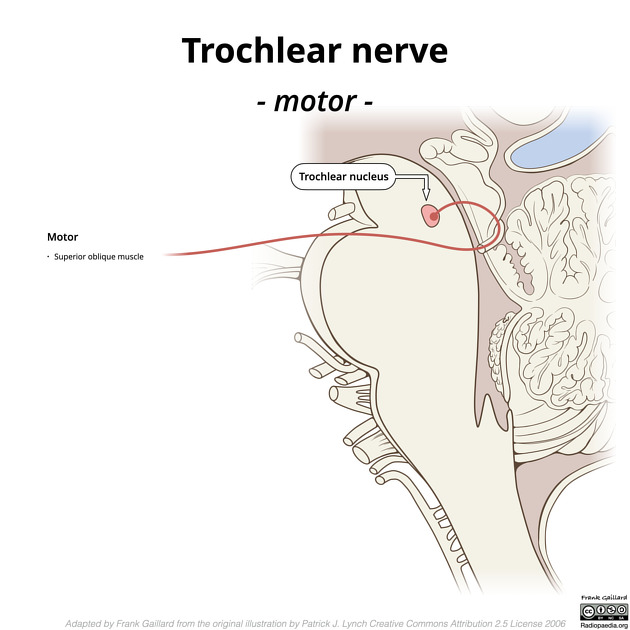
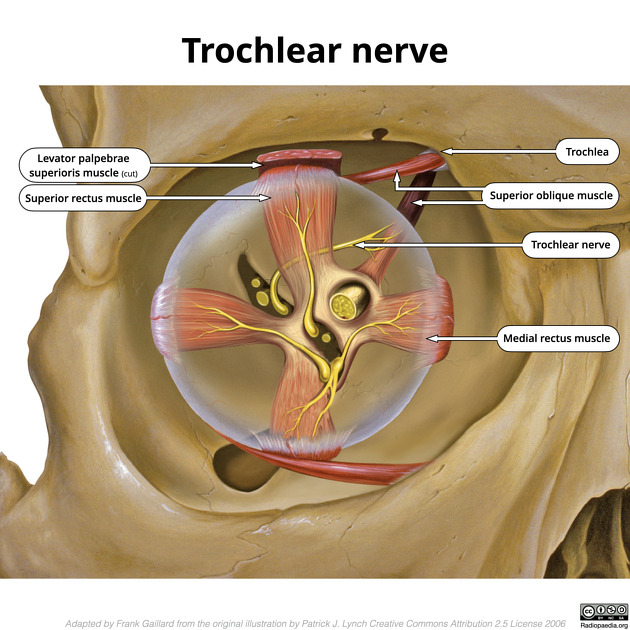
The trochlear nerve is the fourth (CN IV) and thinnest cranial nerve. It exits the midbrain posteriorly, eventually passes into the cavernous sinus and into the orbit where it supplies superior oblique muscle with motor fibres (TA: nervus trochlearis or nervus cranialis IV).
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Nucleus and intraparenchymal portion
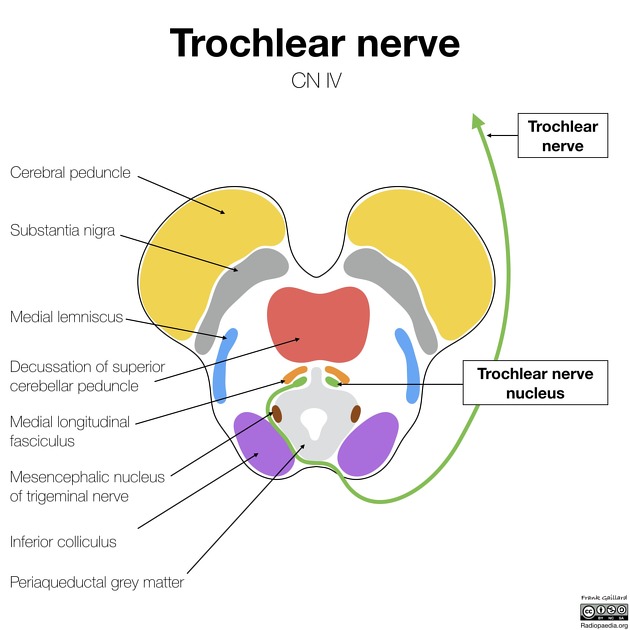
The trochlear nucleus is located in the dorsoventral midbrain, ventral to the periaqueductal grey matter. Its fibres course dorsally and decussate dorsal to the periaqueductal grey matter before exiting the brainstem immediately below the inferior colliculus. It is the only cranial nerve to exit the brainstem posteriorly.
Cisternal portion
The nerve rounds the cerebral peduncles in the ambient cistern. Eventually, along with the oculomotor nerve (CN III), it courses anteriorly between the superior cerebellar artery below and posterior cerebral artery above before piercing the dura between the free and attached edge of tentorium cerebelli.
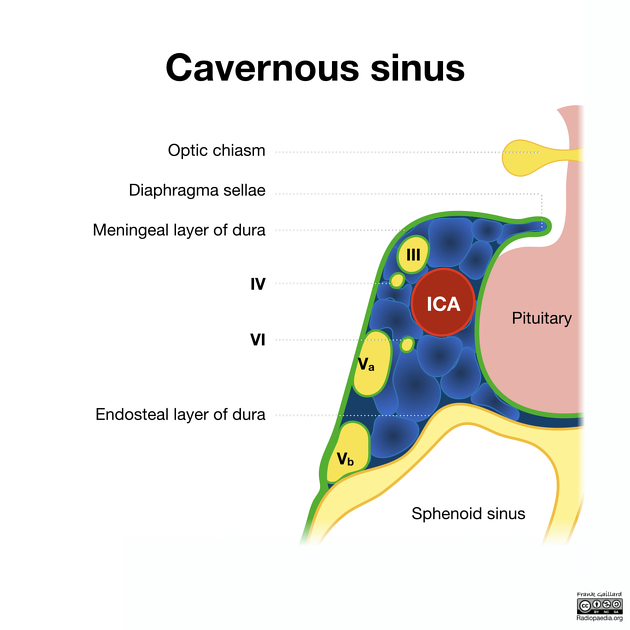
Cavernous sinus portion
Within the cavernous sinus, the trochlear nerve is located initially below the oculomotor nerve in the lateral wall of the sinus, although by the time it reaches the superior orbital fissure, it lies above it (outside the tendinous ring). It is the "Tarts" in this infamous mnemonic.
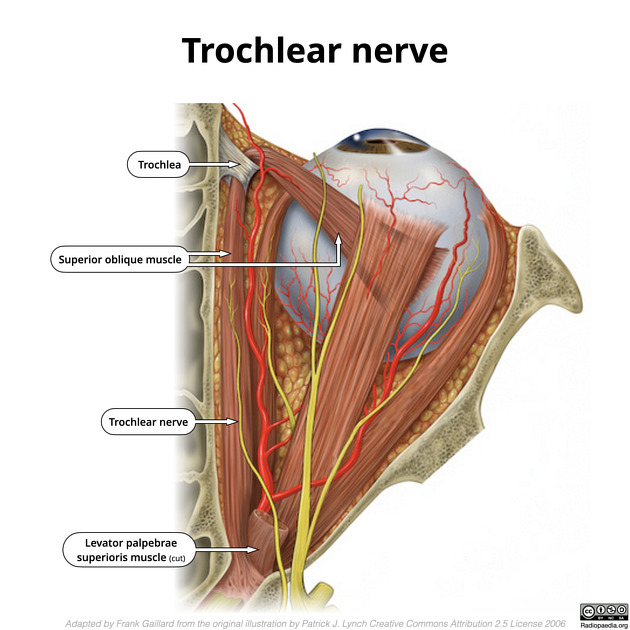
Orbital portion
It enters the orbit outside the tendinous ring, between the superior ophthalmic vein and the superolateral quadrant of the ring. Once in the orbit, it arches up and medially above the superior rectus and levator palpebrae superioris to innervate the superior oblique.
Radiographic features
MRI
Although the nerve is very thin, on high-resolution T2 weighted imaging (e.g. FIESTA/CISS) it can sometimes be visualised as a very thin structure. Dedicated higher-resolution sequences can also be performed if greater detail is required 5.
Related pathology
References
- 1. Chummy S. Sinnatamby. Last's Anatomy. (2011) ISBN: 9780702033957 - Google Books
- 2. Carmine D. Clemente. Anatomy. (2011) ISBN: 9781582558899 - Google Books
- 3. Sheth S, Branstetter B, Escott E. Appearance of Normal Cranial Nerves on Steady-State Free Precession MR Images. Radiographics. 2009;29(4):1045-55. doi:10.1148/rg.294085743 - Pubmed
- 4. R. Shane Tubbs. Nerves and Nerve Injuries. (2015) ISBN: 9780124103900 - Google Books
- 5. Choi B, Kim J, Jung C, Hwang J. High-Resolution 3D MR Imaging of the Trochlear Nerve. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(6):1076-9. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1992 - Pubmed
- 6. FIPAT. Terminologia Anatomica. 2nd Ed. FIPAT.library.dal.ca. Federative International Programme for Anatomical Terminology, 2019. https://fipat.library.dal.ca/TA2/
Incoming Links
- Ambient cistern
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (I)
- Tuberculous meningitis
- Neurovascular compression syndromes
- Inferolateral trunk
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Extraocular muscle nerve supply (mnemonic)
- Basal vein of Rosenthal
- Orbital apex
- Cavernous sinus haemangioma
- Cranial nerve nuclei
- Superior oblique myokymia
- Orbital nerve supply
- Orbital apex syndrome
- Extraocular muscles
- Transition zone (nerve)
- Superior ophthalmic vein
- Trochlear nucleus
- Cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- Superior medullary velum
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.