Umbilical cord
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Knipe H, Murphy A, Lukies M, et al. Umbilical cord. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 25 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-23761
rID:
23761
Article created:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Andrew Murphy had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Andrew Murphy's current disclosures
Revisions:
13 times, by
10 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Synonyms:
- The umbilical cord
- Umbilical cord anatomy
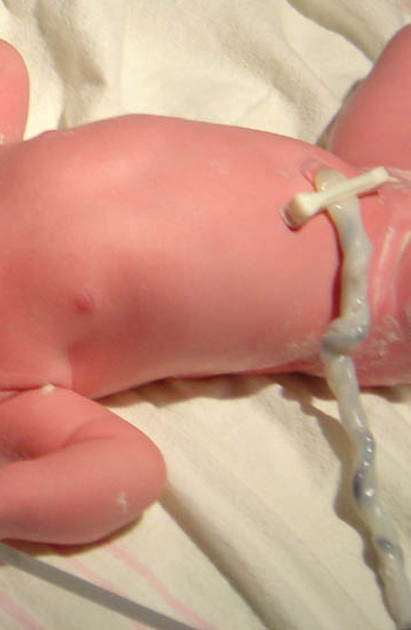
The umbilical cord is a fetal organ that connects the placenta to the developing fetus and is a vital passage for nutrients, oxygen and waste products to and from the fetus.
Gross anatomy
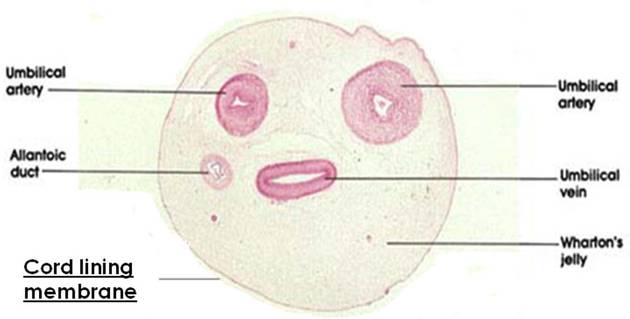
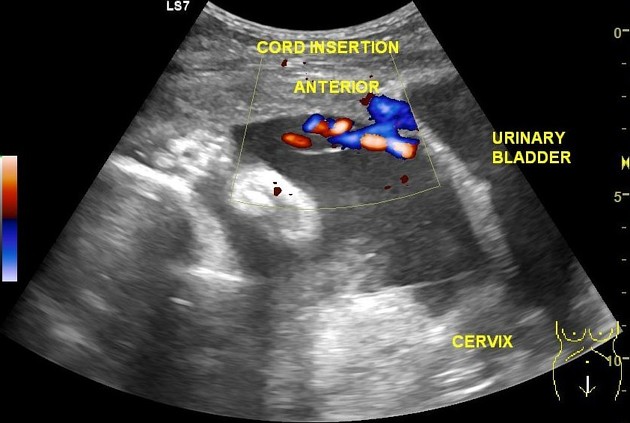
The umbilical cord inserts into the center of the placental bulk and into the fetus at the umbilicus. Variations in insertion can occur. For example, eccentric insertion, marginal insertion and velamentous insertion may be seen 1. It measures 55-60 cm in length with a thickness of 2.0-2.5 cm 3. The normal cord has two arteries and one vein 2-3:
- paired umbilical arteries (branches of the internal iliac artery) carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta
- umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus
Related pathology
References
- 1. Elsayes KM, Trout AT, Friedkin AM et-al. Imaging of the placenta: a multimodality pictorial review. Radiographics. 29 (5): 1371-91. doi:10.1148/rg.295085242 - Pubmed citation
- 2.Yetter JF. Examination of the placenta. Am Fam Physician. 1998;57 (5): 1045-54. Pubmed citation
- 3. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012) ISBN:0521766664. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Articles:
- Cord presentation
- Umbilical cord prolapse
- Umbilical cord entanglement
- Funiculus (disambiguation)
- Umbilical cord haematoma
- Nuchal cord
- Umbilical cord cyst
- Wharton jelly
- Umbilicus
- Umbilical vein
- Myxoid soft tissue tumours
- Amniotic fluid index
- Umbilical artery
- Long umbilical cord
- False umbilical cord knot
- Foramen ovale (cardiac)
- Placenta
- Umbilical cord pseudocyst
- True umbilical cord knot
- Forked umbilical cord
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.