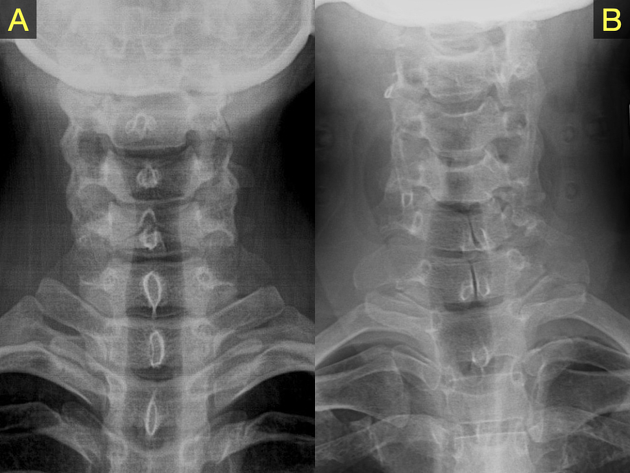
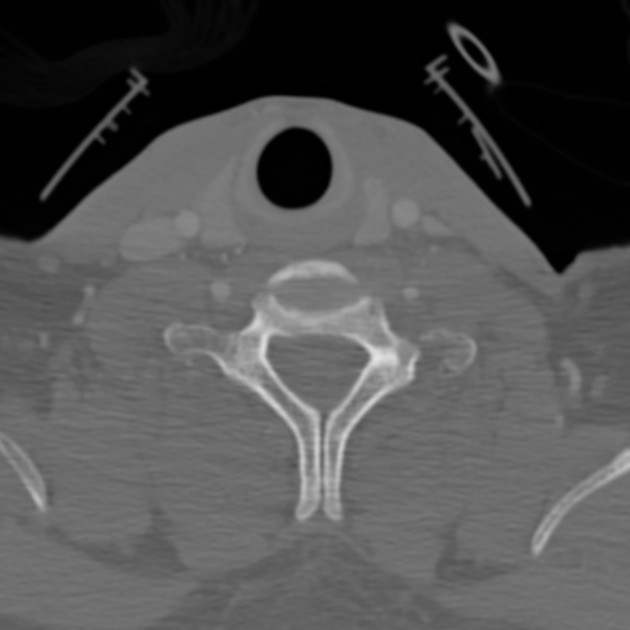
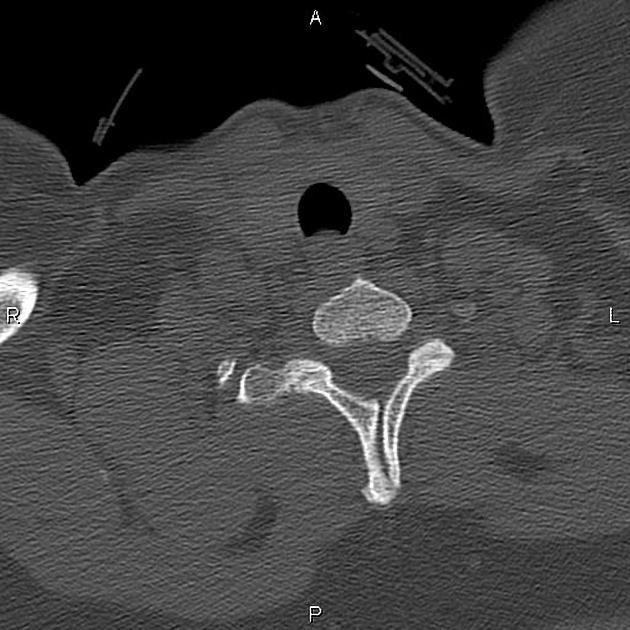
Unfused spinous process
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Anon Ny Mous had no recorded disclosures.
View Anon Ny Mous's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Unfused spinous processes
The unfused spinous process, which is failure of fusion of the vertebral arch, is a relatively common anatomical variant and is part of the spectrum of spina bifida occulta.
This should be differentiated from accessory ossicles of the spinous process, which appear after the non-fusion of the secondary ossification centre (or centres in bifid spinous processes). These appear as a well-corticated fragment adjacent to the tip of the spinous process with a vertical or near-vertical lucency.
The importance lies in patients with potentially traumatic spinal injuries, in which it is important to identify this variant and avoid the potential pitfall of diagnosing a fracture. A well-defined cortical margin is a helpful clue.
Differential diagnosis
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Theodore E. Keats, Mark W. Anderson. Atlas of Normal Roentgen Variants That May Simulate Disease. (2012) ISBN: 9780323073554 - Google Books
- 2. Mellado J, Larrosa R, Martín J, Yanguas N, Solanas S, Cozcolluela M. MDCT of Variations and Anomalies of the Neural Arch and Its Processes: Part 1--Pedicles, Pars Interarticularis, Laminae, and Spinous Process. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197(1):W104-13. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5803 - Pubmed
- 3. Paul Butler. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (1999) ISBN: 9780521481106 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Spine
-
osteology
- vertebrae
- spinal canal
- cervical spine
- thoracic spine
- lumbar spine
- sacrum
- coccyx
-
anatomical variants
- vertebral body
- neural arch
- transitional vertebrae
- ossicles
- ossification centres
- intervertebral disc
- articulations
- ligaments
- musculature of the vertebral column
- muscles of the neck
- muscles of the back
-
suboccipital muscle group
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- splenius capitis muscle
- splenius cervicis muscle
- erector spinae group
- transversospinalis group
- quadratus lumborum muscle
-
suboccipital muscle group
- spinal meninges and spaces
-
spinal cord
- gross anatomy
-
white matter tracts (white matter)
- corticospinal tract
- anterolateral columns
- lateral columns
-
dorsal columns
- fasiculus gracilis (column of Goll)
- fasiculus cuneatus (column of Burdach)
- grey matter
- nerve root
- central canal
- functional anatomy
- spinal cord blood supply
- sympathetic chain




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.