CT
What is the role of the non-contrast CT of the chest?
The non-contrast imaging of the chest is an important part of the protocol for concerns regarding acute aortic syndrome. This enables one to assess for intra-mural haematoma, which can occur in isolation without a dissection flap as part of the spectrum of acute aortic syndrome.
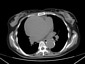
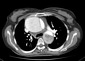
There is dilatation of aortic root, ascending aorta, aortic arch and descending aorta.
An intimal flap is seen extending from the aortic root proximally to below the origin of the renal arteries distally dividing the aortic lumen into true and false lumens (Stanford Type A and type I DeBakey classification).
Right brachiocephalic, left common carotid, left subclavian, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric and bilateral renal arteries are seen arising from true lumen.
There is significant narrowing at the origin of celiac trunk of abdominal aorta. Atherosclerotic wall calcification is noted at origin of left renal artery.
Cardiomegaly with dilatation of all cardiac chambers is noted.