CT
Why is there an upper lung predominance in most pneumoconioses?
Because in the upper lobes there is relatively overventilation (ratio of ventilation to perfusion, 3:1) and less lymphatic particle clearance, compared with the lung bases (ratio 0,6:1).
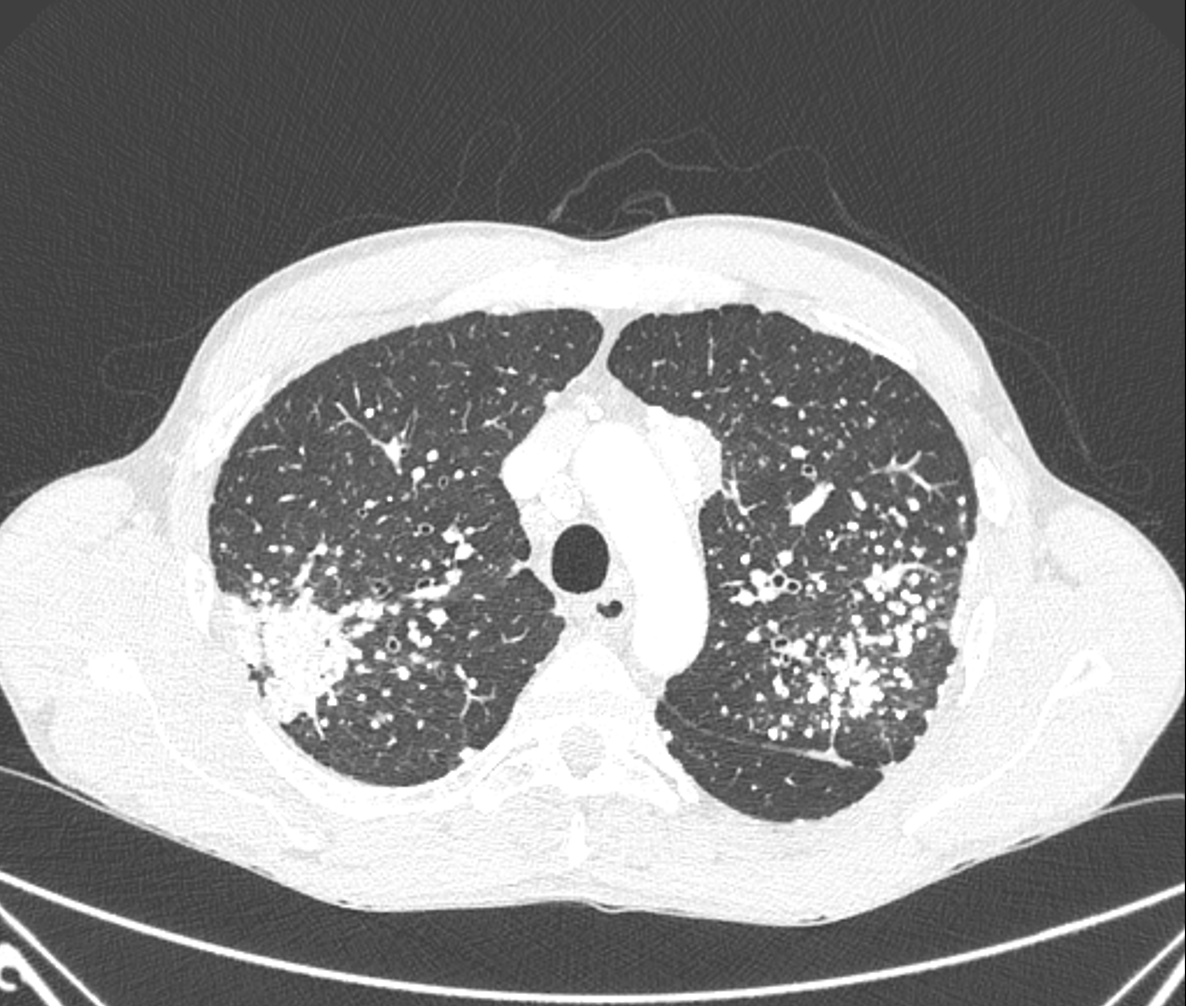
CT confirms the presence of innumerable bilateral pulmonary calcified nodules, predominantly in the upper and posterior zones. These nodules have a centrilobular and subpleural distribution. Two partially calcified mass-like conglomerates in both upper lobes with associated radiating strands can be observed (progressive massive fibrosis).
There are also mediastinal and hilar "egg-shell" calcified lymph nodes.