Presentation
Acute abdominal pain and hypotension.
Patient Data
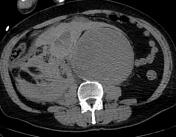

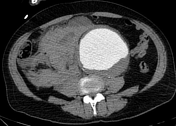

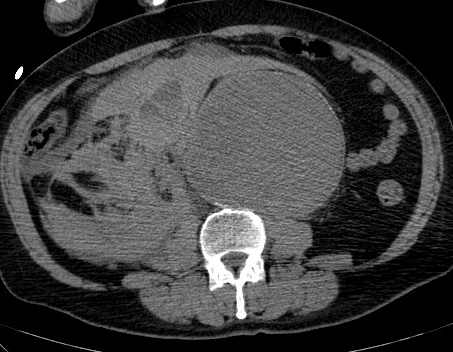
Infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm, measuring up to 11 cm in AP diameter and about 17 cm in cc dimension, with peripheral discontinuous wall calcification, extending from below the level of renal artery origins to the aortic bifurcation, has a partially thrombosed lumen. It is associated with large amounts of right-sided hemoperitoneum and hemoretroperitoneum extending to a right-sided inguinal hernia, most likely due to the mentioned abdominal aortic aneurysm leak. It shows a minimal increase in density after contrast administration, suggesting active bleeding.
Case Discussion
Abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture is a surgical emergency with high mortality rate.
This patient passed away from hypovolemic shock before reaching the operating room.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.