Presentation
Headaches, low-grade fever, and deterioration of the level of consciousness.
Patient Data
Age: 20 years
Gender: Female
From the case:
Cerebral tuberculosis










Download
Info
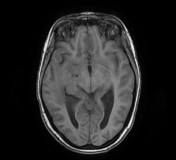
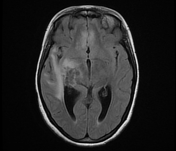
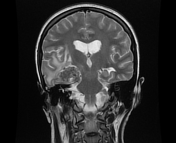
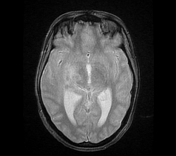
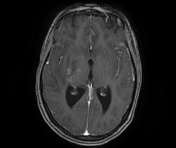
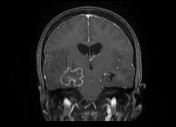
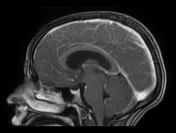
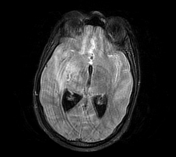
The MRI sequences demonstrate:
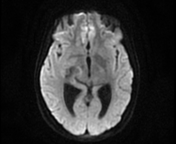
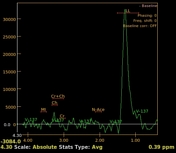
- a lobulated intra-axial mass in the right temporal region isointense to the cortical grey matter on T1WI with peripheral hyperintense rim (paramagnetic material), hypointense on T2WI/FLAIR with a cluster of ring enhancement on postcontrast sequences. A large area of surrounding vasogenic oedema is noted extending to the internal/external capsules with a mass effect on the temporal horn and midbrain. The multivoxel MR spectroscopy reveals a dominant peak in Lipids / Lactate (LL). Findings are most consistent with tuberculous granuloma (or tuberculoma).
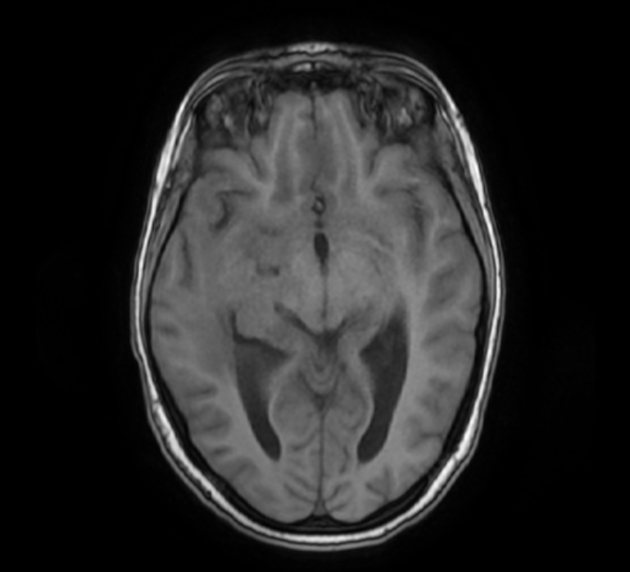
- the cortical grey matter at the frontal parasagittal regions appears thickened isointense on T1WI, hyperintense on T2WI/FLAIR with mild gyral enhancement on postcontrast sequences and restricted diffusion indicating most likely a focal cerebritis.
- meningeal enhancement of basal subarachnoid cisterns, along the middle cerebral arteries to the Sylvian fissures and cerebral hemispheres well-visualised on postcontrast FLAIR fat saturation (despite the motion artifact), in keeping with meningitis.
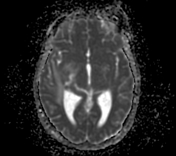
- Mild dilatation of the 3rd and lateral ventricles in keeping with obstructive hydrocephalus.
Case Discussion
Case showing the MRI features of cerebral tuberculosis associating cerebral tuberculoma (or tuberculous granuloma), focal cerebritis, and tuberculous meningitis.
The CSF analysis with culture was positive tuberculous origin.
Additional contributor: A. Ramdani, MD




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.