Presentation
Left lower eyelid swelling since two months.
Patient Data
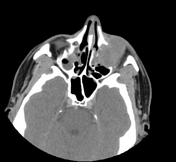

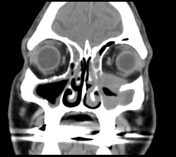

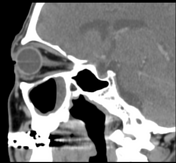

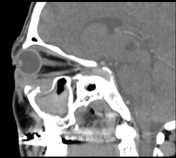

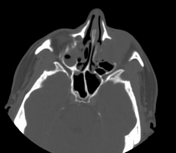

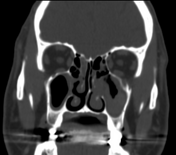

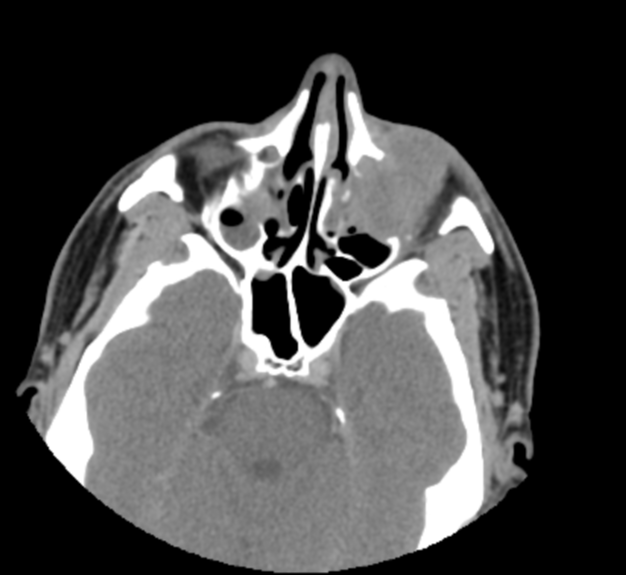
Left maxillary sinusitis with internal hyperdense material, associated with soft tissue lesions at the anterior superior aspect of the antrum which extends anteriorly to the lower eyelid, with adjacent bone erosions of the anterior and superior walls of the maxillary antrum.
Mild right maxillary, bilateral ethmoid and to a lesser extent left sphenoid sinusitis.
Radiological findings suggest left maxillary invasive fungal sinusitis. Sinonasal carcinoma is also another possibility.
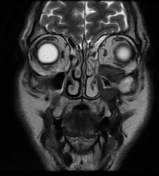

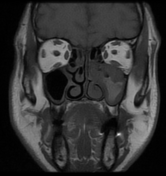

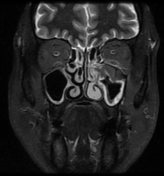

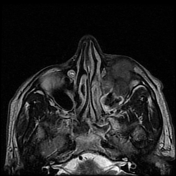

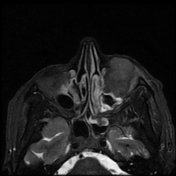

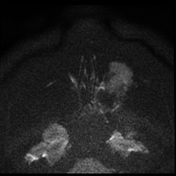

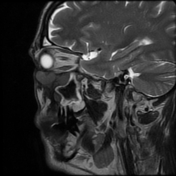

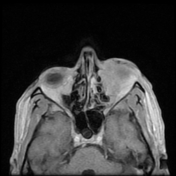

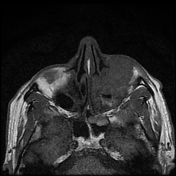

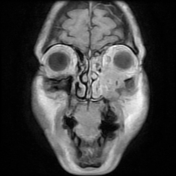

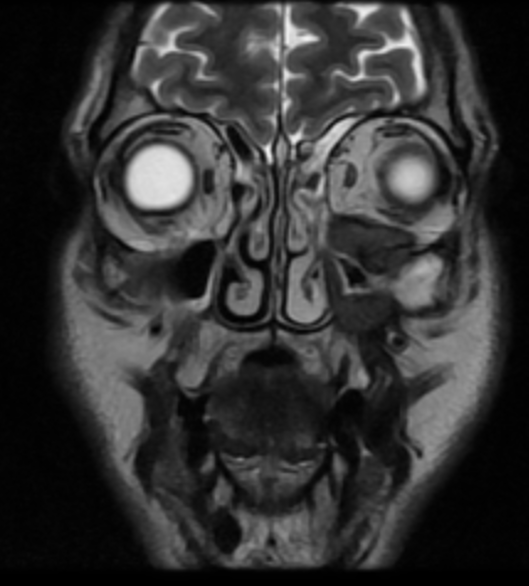
The soft tissue lesions elicit low signal on T1, T2 & STIR WI. It shows intense post contrast enhancement. It shows small intra-orbital extension along the lower aspect of the orbit and the lower eyelid.
Despite the bony destruction and the associated extra-sinus soft tissue extension; the low T2 signal of the lesions was suggestive of invasive fungal sinusitis rather than a neoplastic process.
Case Discussion
Biopsy revealed mucormycosis.
Chronic invasive fungal sinusitis is a form of invasive fungal sinusitis.
Patients are usually immunocompetent or have a milder level of immunocompromise. There may be a history of chronic sinusitis.
On CT, it shows:
mottled lucencies or irregular bone destruction may be seen
bone erosion localised to the area of extrasinus extension
extrasinus component of the disease more prominent than the intrasinus component
there may also be sclerotic changes in the bony walls of the affected sinuses representing chronic disease
On MRI, typical markedly low signal on T2 WI.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.