Presentation
Respiratory distress at birth
Patient Data
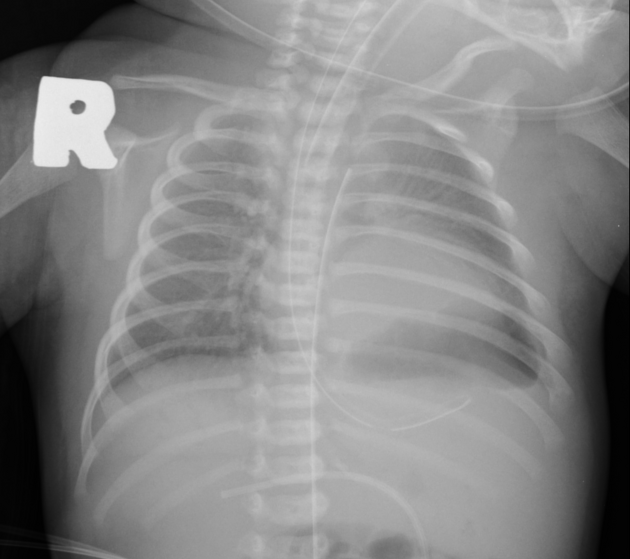
Indistinct margin of left hemidiaphragm. Homogeneous opacity at left mid lung zone. Normal left heart border is obliterated.
Nasogastric feeding tube with the tip below the supposed left hemidiaphragm. Stomach gas is not present with paucity of bowel gas at the left hypochondrium.
Ground-glass opacity at the left upper lung zone.
Suboptimal high position of the umbilical artery catheter (T3 level).
Endotracheal tube in situ with tip 1 cm above the carina.
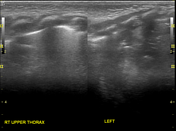
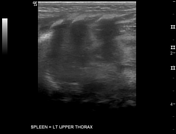
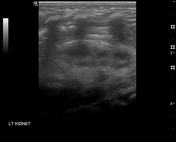
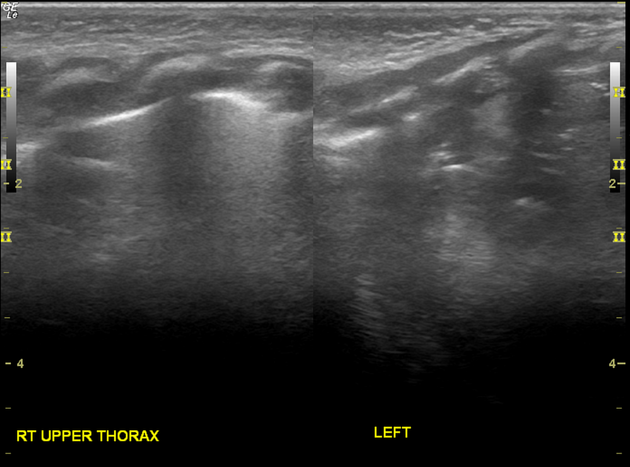
Absence of lung sliding sign or the normal pleural line at the left lower hemithorax.
Spleen is located within the mid left hemithorax. High position of the left kidney. Unable to visualise obvious bowel loops in left hemithorax.
Very thin 0.1 cm membrane at the location of left hemidiaphragm separates the spleen from the left collapsed lung. This thin left hemidiaphragm maintained normal respiratory motion.
Right hemidiaphragm measures 0.3 cm with normal respiratory motion.
Chest radiograph and the ultrasound thorax suggest the diagnosis of congenital diaphragmatic hernia or congenital eventration of the diaphragm.
Proceeded with MRI thorax/abdomen (respiratory trigger) - limited sequences.
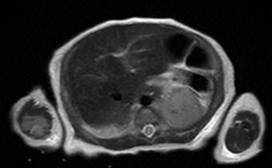

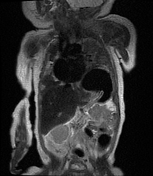

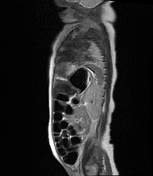

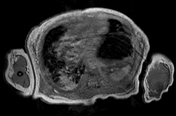


Focal elevation of the posterolateral aspect of left hemidiaphragm up to T5 vertebral level. No obvious discontinuity or defect seen at the left hemidiaphragm.
Herniation of the fundus and body of stomach, spleen and upper pole of left kidney through the defect with slight mediastinal and cardiac shift to the right side.
Consolidation and atelactasis at left lower lobe with reduced lung volume. Normal aerated left upper lobe.
Focal lung consolidation at the right lower lobe with minimal right pleural effusion.
Cardiomegaly.
Case Discussion
Imaging findings are suggestive of congenital eventration of left hemidiaphragm with left lower lobe pulmonary hypoplasia.
Right lower lobe lung consolidation may represent aspiration pneumonia.
The differential diagnosis to consider is the more common congenital diaphragmatic hernia (Bochdalek hernia). Radiologically, it is challenging and sometimes difficult to differentiate the two.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.