Presentation
Chromosomal abnormality, polymalformative syndrome. Difficulty in rotating the forearm.
Patient Data
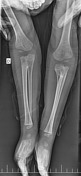
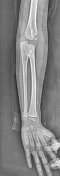
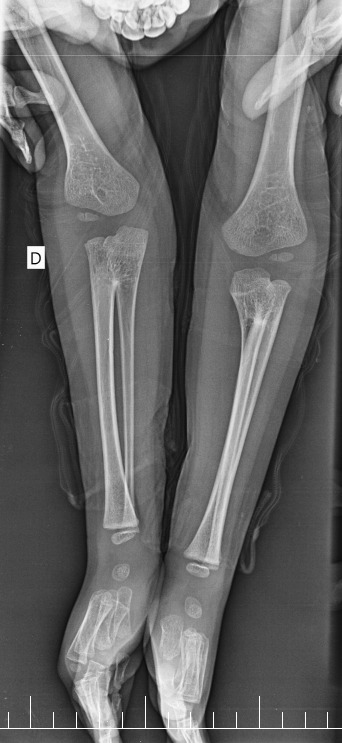
Complete osseous fusion between the proximal third of the radius and ulna, with absence of an interosseous space.
The distal radio-ulnar joint and the radio-humeral joint are preserved.
No evidence of erosive or destructive lesions.
The soft tissues of the forearm are unremarkable.
Note:
Growth retardation was observed, with bone age estimated at 2 years using the Greulich and Pyle method.
Case Discussion
Radioulnar synostosis is an uncommon condition in which the radius and ulna are abnormally fused, limiting normal rotational movement of the forearm. Although most often congenital, radioulnar synostosis can also occur following trauma or fracture of the forearm.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.