Presentation
Acute onset motor aphasia after coronary angiography.
Patient Data
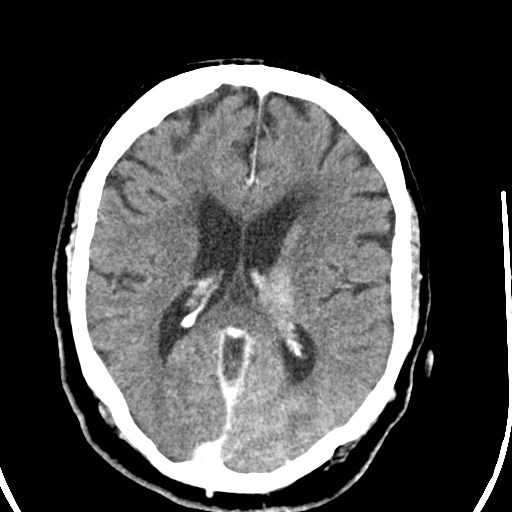
Intravascular contrast can be seen due to coronary angiography performed 2 hours earlier.
There is subarachnoid hyperdensity in the left parietal and occipital lobes and cortical hyperdensity and edema in the left parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes, left thalamus, and both cerebellar hemispheres, all due to contrast leakage.
There is also periventricular white matter hypodensity due to chronic small vessel ischemia.
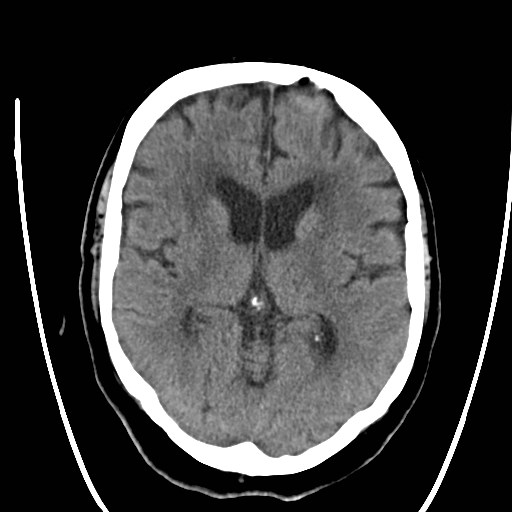
Follow up CT scan performed 6 days later shows resolution of the subarachnoid and cortical hyperdensities. As the only sequela, there is a cortico-subcortical hypodense area in the caudal part of the left cerebellar hemisphere related to subacute infarction.
Case Discussion
This 70-year-old male patient underwent a coronary angioplasty with stent placement in the left anterior descending artery. One hour after the procedure, he presented with acute onset motor aphasia, nausea, and hypotension. The patient was treated with intravenous fluid therapy and antiemetic, with complete recovery of symptoms in the next 4-6 hours.
The diagnosis of contrast-induced neurotoxicity was confirmed by CT findings and spontaneous and rapid resolution of the neurological symptoms.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.