Presentation
Dysphagia more to solids. Sensation of a lump in the throat.
Patient Data


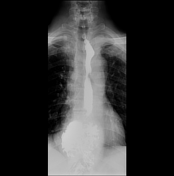

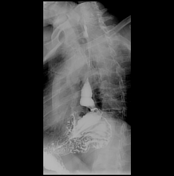

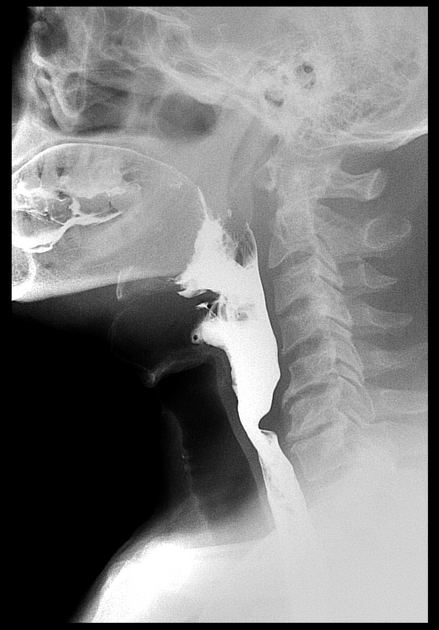
Barium swallow examination revealed:
focal impression at the posterior aspect of the cervical oesophagus opposite C5-6 level (cricopharyngeal muscle spasm)
evidence of a large hiatus hernia with part of the gastric fundus and the gastro-oesophageal junction seen above the diaphragm (mixed hiatus hernia)
Case Discussion
Dysphagia is defined as difficulty in swallowing. The cricopharyngeal muscle or the upper oesophageal sphincter is normally persistently contracted except during swallowing. Cricopharyngeal muscle spasm results from failure of complete relaxation of the muscle and/or its early contraction.
A hiatus hernia is defined as a protrusion of the upper part of the stomach into the thoracic cavity. There are four types: sliding, para-oesophageal, mixed and mixed with herniation of other viscera. Patients can complain of reflux symptoms all in types except in the para-oesophageal type as the gastro-oesophageal junction is at its normal intra-abdominal site (i.e. is not intra-thoracic).
Special thanks to Dr Bahaa Al-Dein Mahmoud.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.