Presentation
Headaches.
Patient Data
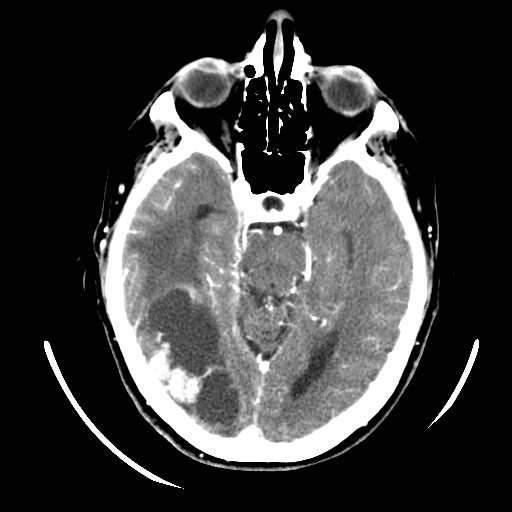
CT-scan shows a voluminous parieto-occipito-temporal hypodense lesion with intense focus of nodular enhancement in its lateral portion, associated with vasogenic edema. The density is slightly higher than CSF. There is an associated diffuse ipsilateral leptomeningeal enhancement & slight right temporal uncal herniation. The right lateral ventricle is sequestred.
The differential diagnosis for cystic intra-axial lesions with nodular enhancement portions includes :
- isolated cystic metastasis
- ganglioglioma
- oligodendroglioma
- pilocytic astrocytoma : usually posterior fossa & more common in children
- DNET : usually little if any enhancement
The patient had a known ovarian cancer. The most probable diagnosis remains metastases in this patient with possible leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. MRI was recommended.
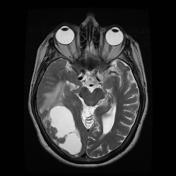

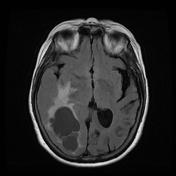

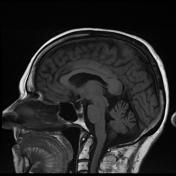

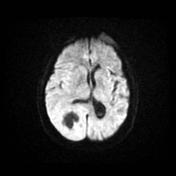

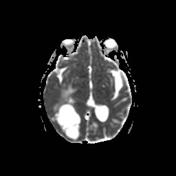

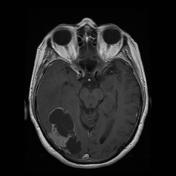

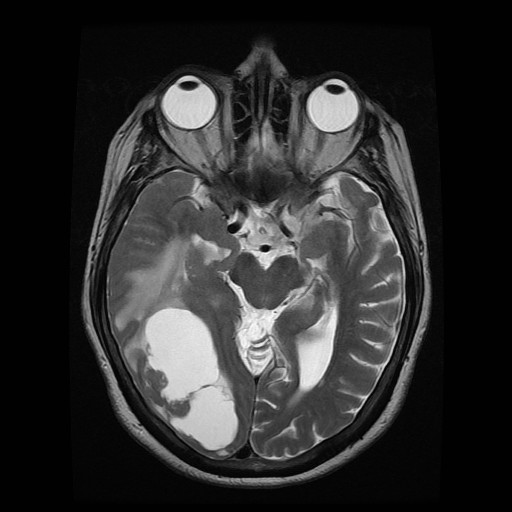
MRI confirms the multicystic component of the lesion, centrally. There is a restriction to diffusion on DWI/ADC only involving the enhancing nodule. Right temporal uncal herniation is more obvious.
The differential diagnosis remains the same. Leptomeningeal enhancement is harder to appreciate. Metastasis remains the most probable diagnosis.
Case Discussion
The histological diagnosis was metastasic ovarian carcinoma.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.