Presentation
Gunshot wound to the head, frontal to occipital region, with prior surgery for bone removal on day 4.
Patient Data
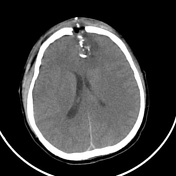

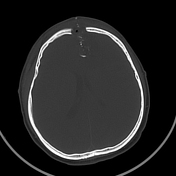

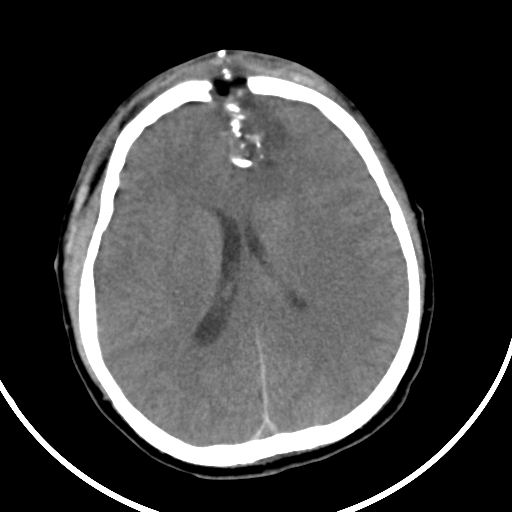
Penetrating brain injury is caused by a gunshot wound. The bullet's trajectory can be visualised, extending from the frontal to the occipital region, resulting in damage to the frontal skull bone and brain parenchyma (haemorrhage with cerebral oedema) along its path. The bullet is lodged in the occipital parenchyma, causing an artifact, without exiting the skull. Multiple high-density foreign bodies are present inside the skull and subcutaneous tissue, including metal fragments and shattered skull bone fragments. There is soft tissue swelling and subcutaneous emphysema in the bilateral frontal regions.
Case Discussion
The patient passed away a few days later.
Gunshot injuries to the head are classified as high-velocity penetrating brain injuries, which result in severe and complex damage and are associated with a high mortality rate.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.