Presentation
Trauma.
Patient Data



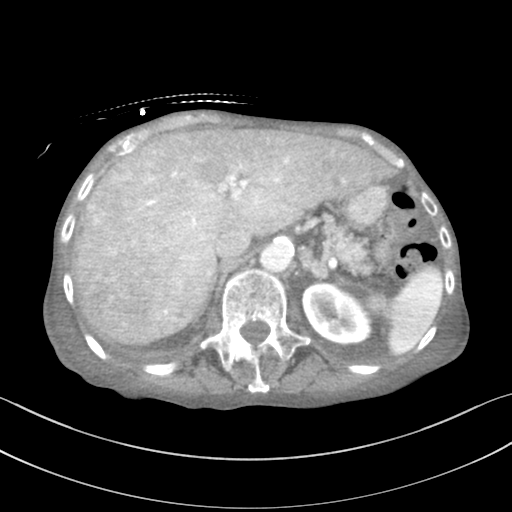
Bilateral pleural effusions, larger on the right, are associated with basal atelectasis: these findings are most likely due to pulmonary oedema. Cardiac enlargement and previous sternotomy indicate underlying cardiac disease.
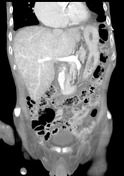
Fluid within the abdomen and pelvis is low density, keeping with ascites rather than haemoperitoneum. Heterogeneous enhancement of the liver, which appears enlarged, represents congestive hepatopathy.
No evidence of traumatic injury to the liver, spleen, pancreas, or kidneys. Calcification in the pancreatic head may be due to previous pancreatitis. The adrenals, gallbladder and bladder are unremarkable. Uncomplicated sigmoid diverticulosis, otherwise the bowel has a normal appearance.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.