Presentation
Bilateral papilledema grade 3
Patient Data
Age: 20 years
Gender: Female
From the case:
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension









Download
Info
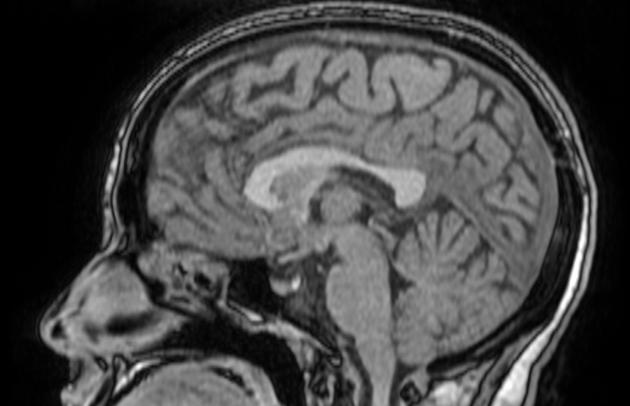
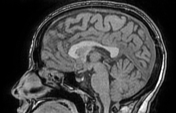
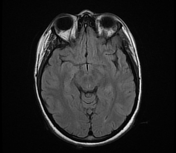
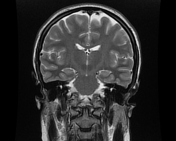
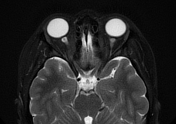
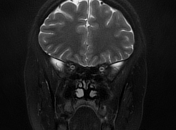
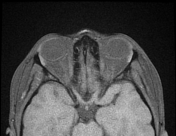
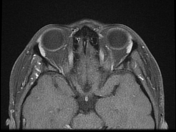
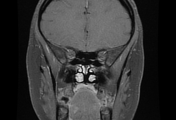
The MRI sequences demonstrate:
- flattening of the posterior sclera bilaterally
- protrusions of the optic nerve heads
- vertical tortuosity of the optic nerves
- enhancement of the prelaminar (intra-ocular) optic nerves well-visualized on postcontrast axial T1 fat saturation
- slight enlargement of the subarachnoid space around the optic nerves
- Partially empty sella turcica (pituitary gland's height=4.5 mm)
- the cerebral venous sinuses are patent on postcontrast sequences with no significant stenosis (MRV was not performed)
- no mass lesion is seen at the infra- or supratentorial level.
Case Discussion
MRI findings suggestive of an idiopathic intracranial hypertension
In the absence of a cause for intracranial hypertension, the imaging features should suggest an idiopathic origin




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.