Presentation
Sudden onset of severe headaches, vomiting
Patient Data
Age: 35 years
Gender: Male










Download
Info
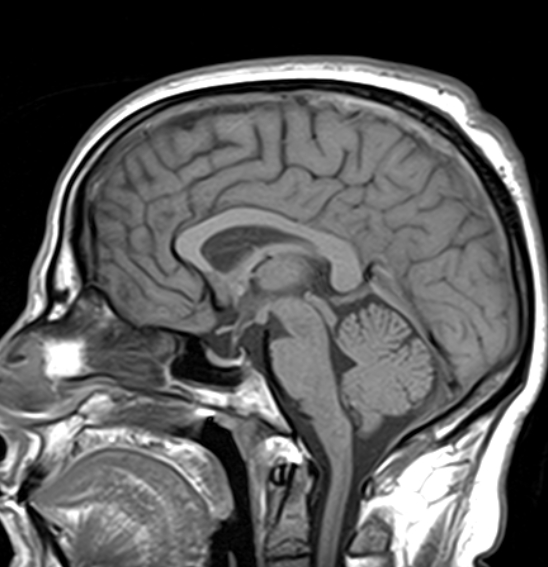
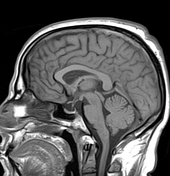
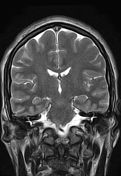
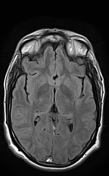
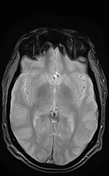
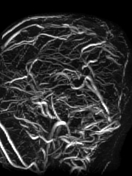
The MRI sequences demonstrate:
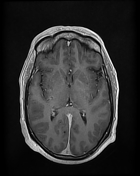
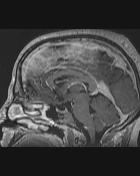
- Thrombosis of the cerebral venous sinuses mainly the superior sagittal sinus, transverse/sigmoid sinuses, and right jugular vein which appear of high signal on T1WI/FLAIR and iso-to high signal on T2WI (subacute phase) with loss of their signal void on contrast MR venography.
- signs of secondary intracranial hypertension
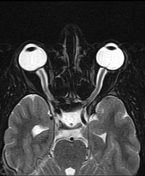
- enlarged subarachnoid space around the optic nerves
vertical tortuosity of the optic nerves
flattening of the posterior sclera bilaterally
- intraocular protrusion of the optic nerve head
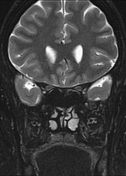
- Partially empty sella turcica
- moderate enlargement of the Meckel cave mainly on the left
Case Discussion
MRI features typical of secondary intracranial hypertension due to cerebral venous thrombosis




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.