Presentation
Sudden-onset of right hemiparesis with dysarthria in a hypertensive and diabetic patient.
Patient Data
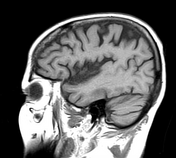

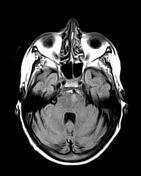

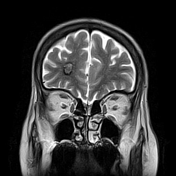

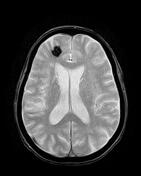



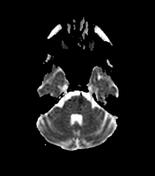



Lesion of the left lateral aspect of the pons of low signal intensity on T1, high signal intensity on T2 and FLAIR with restricted diffusion in keeping with an acute stroke.
Well-defined subcortical right frontal lesion of mixed-signal intensity centrally on both T1, T2 and FLAIR with prominent blooming on gradient echo sequence and no surrounding edema or enhancement on postcontrast sequence, in keeping cavernoma (incidental finding).
Cerebral volume loss with small vessel ischemic changes as well as old lacunar infarcts in the basal ganglia.
Case Discussion
Lateral pontine syndrome, also known as Marie-Foix syndrome or Marie-Foix-Alajouanine syndrome, refers to one of the brainstem stroke syndromes of the lateral aspect of the pons. It is due to occlusion of perforating branches of the basilar and anterior inferior cerebellar (AICA) arteries.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.