Presentation
38-week gestation. Day 2 follow up x-ray. To assess ETT and UVC.
Patient Data
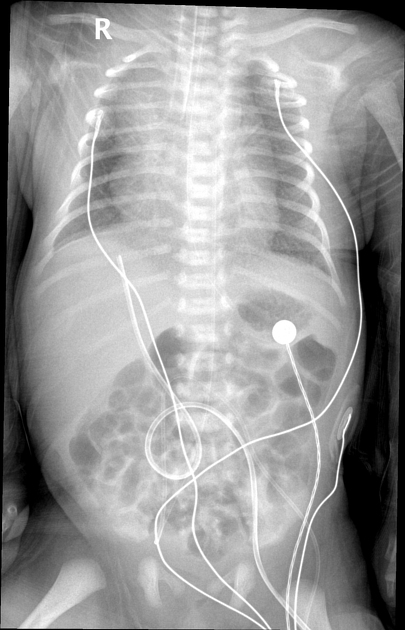
The lung fields are hyperinflated with mild surfactant deficiency disorder. There is a normal cardiomediastinal contour. The ETT is at the carina and needs to be retracted. There is mild right-sided rotation and possible developing right-sided volume loss and tracheomediastinal displacement due to the low-lying ETT.
The nasogastric tube tip is at the gastric fundus and can be more distally inserted. The umbilical arterial catheter tip is at the T5 vertebral body level.
The umbilical venous catheter is malpositioned and within a right portal venous branch. There are no intrahepatic gaseous lucencies.
The bowel gas pattern is nonspecific.
The bones and soft tissues appear normal.
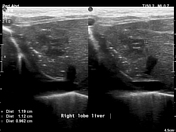

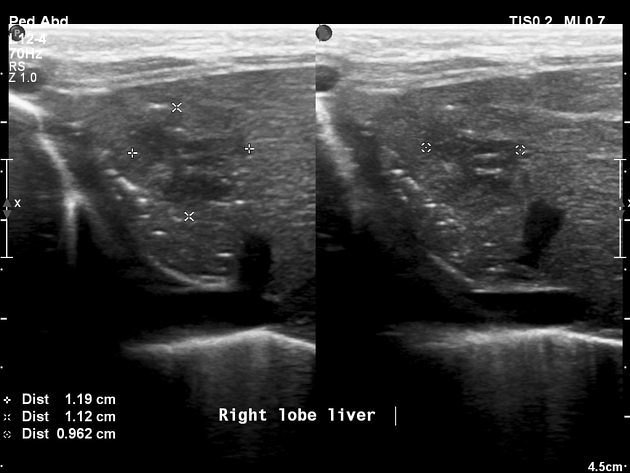
Portable ultrasound confirmed an intrahepatic fluid collection (TPNoma). This appears heterogeneous in sonographic appearance with a hypoechoic centre and a vague hyperechoic and lobulated rim. The malpositioned UVC is seen traversing the fluid collection.
Ultrasound is otherwise normal.
Case Discussion
Features consistent with a subacute intrahepatic fluid collection (TPNoma) relating to infusion of hypertonic fluids (saline/ other) and/or TPN in a malpositioned UVC.
The clinical absence of septicaemic symptoms or elevated inflammatory/ septic markers in a stable infant further re-affirm the likely absence of a hepatic abscess or an infected fluid collection.
Large TPNomas are of concern and can accompany a hepatic laceration and perihepatic ascites1. With the removal or the correct resiting of the malpositioned UVC, these large collections often resolve spontaneously completely or evolve into smaller, irregular, echogenic lesions with calcifications and posterior acoustic shadowing 1.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.