Presentation
Nausea and anorexia worsening for 1 week. 2 days of right upper quadrant pain.
Patient Data
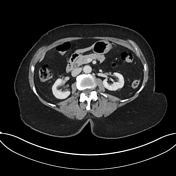

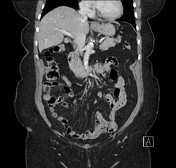

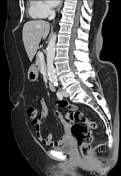

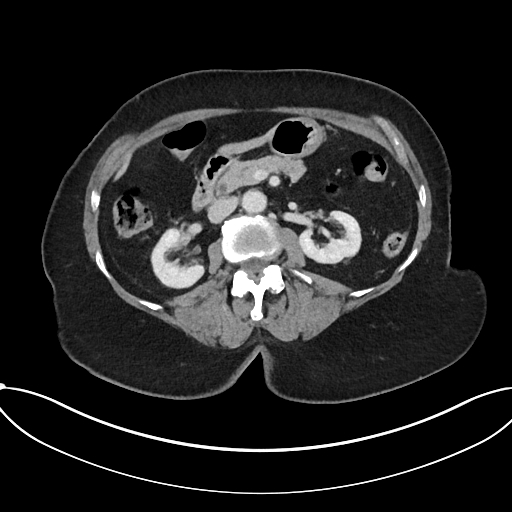
Multiple calcified gallstones and sludge in the gallbladder with mild pericholecystic fat stranding. There is a partially calcified 15 mm stone within the gallbladder neck. Generalized intrahepatic duct dilatation and dilatation of the common hepatic duct, with a normal caliber common bile duct, is due to extrinsic compression from the stone within the gallbladder neck. Mild prominence of the main pancreatic duct. Pancreatic tail cystic lesion measures 13 mm.
Large multifibroid uterus. The remaining solid organs are unremarkable. The bowel is normal as is the appendix. No free fluid or free gas. No lymphadenopathy.
Umbilical fat-containing hernia appears uncomplicated. Lung bases are clear. No aggressive osseous lesions. Multilevel lumbar degeneration.
Impression:
intrahepatic duct dilatation due to obstruction of the common hepatic duct by a 15 mm gallbladder neck calculus consistent with Mirizzi syndrome. Cholelithiasis and mild CT features of acute cholecystitis
small pancreatic tail cystic lesion is non specific
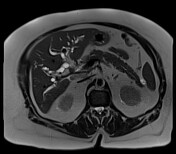

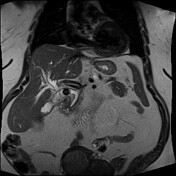

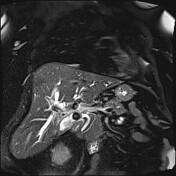


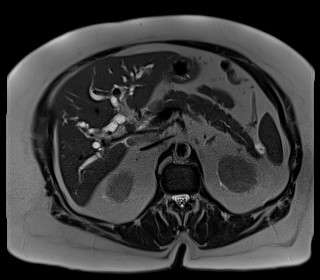
The degree of intrahepatic biliary dilatation has increased slightly since the CT, secondary to a 15 mm stone impacting the gallbladder neck and obstructing the adjacent common bile duct (Mirizzi syndrome). Four other similar sized calculi noted within the gallbladder fundus along with mixed signal intensity sludge.
Incidental 10 x 20 mm cystic lesion within the pancreatic body communicates with the nondilated major pancreatic duct via a small branch duct.
Impression:
confirmation of Mirrizi syndrome - type 1
incidental pancreatic cystic lesion likely a branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
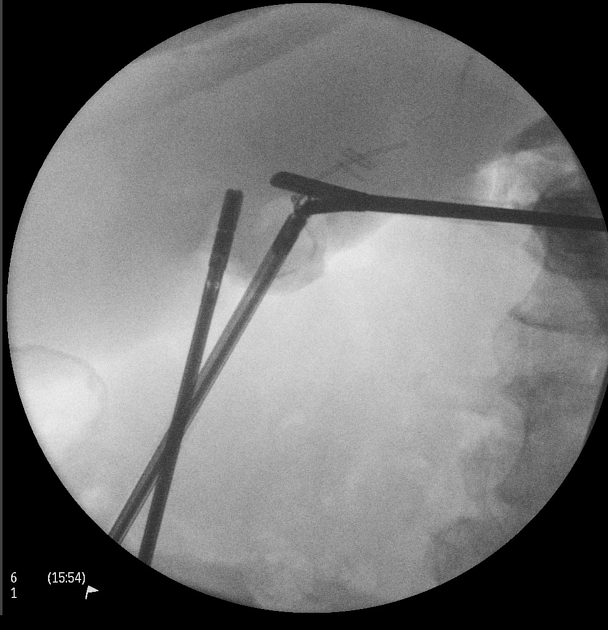
Intraoperative cholangiogram shows a large stone in the distal cystic duct impinging the common hepatic duct, causing extra and intrahepatic duct dilatation.
Case Discussion
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy was performed which confirmed several large gallstones and sludge in an inflamed gallbladder. The cystic duct was cannulated and intraoperative cholangiogram showed a large stone impacting the duct and causing extrinsic compression of the common hepatic duct and intrahepatic duct dilatation. The stone was removed without complication.
Gallbladder histology revealed adenocarcinoma.
The patient had an uneventful post operative course.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.