Presentation
History of old stroke with left-sided weakness.
Patient Data
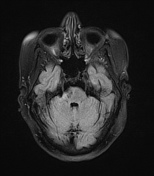

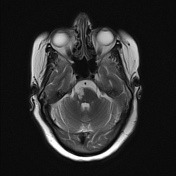

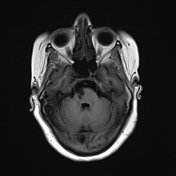


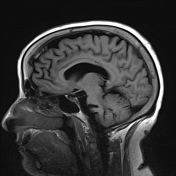

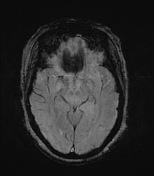

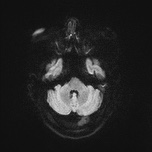

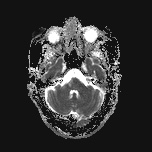

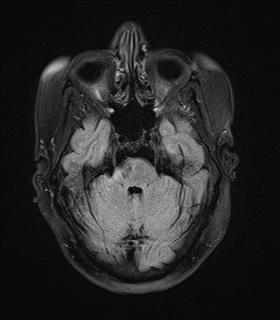
A high T2 signal lesion is noted at the right side of the lower pons with hypointense signal on FLAIR and T1 reflecting encephalomalacia with no diffusion restriction, mostly representing old pontine infarction.
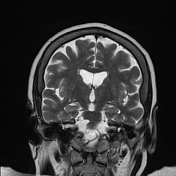
Involutional brain changes seen as widened sulci and slightly dilated ventricles. Multiple high T2 and FLAIR white matter foci involving periventricular white matter, corona radiata and centrum semiovale reaching subcortical white matter, mostly due to chronic cerebral small vessel disease.
Incidental note of thickened inner table of both frontal bones with overgrowth and irregular inner surface, in keeping with hyperostosis frontalis interna.
Case Discussion
Typical features of old pontine infarction, cerebral small vessel disease and hyperostosis frontalis interna. Pontine infarction is the territory of perforating branches of basilar artery.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.