Presentation
Pelvic pain.
Patient Data
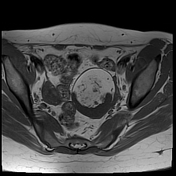

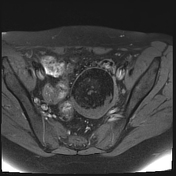

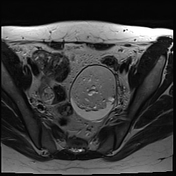

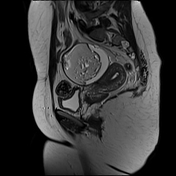

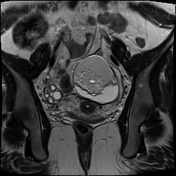

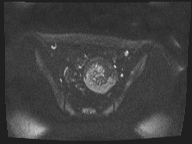

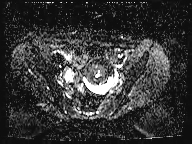

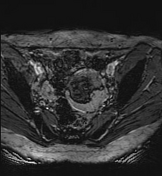

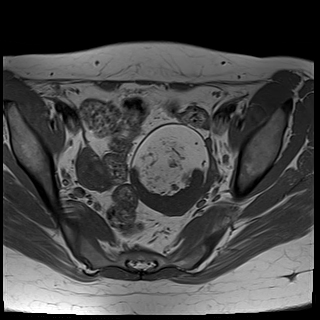
A large left ovarian cystic lesion with stretched ovarian parenchyma around its wall. It shows a predominate fat signal component (high signal intensity on T1 and T2 with complete suppression of signal on T1 fat sat sequence) and a fluid component (hypointense signal on T1 and high signal intensity on T2 and isointense signal on T1 fat sat sequence), with a fat-fluid level. No diffusion restriction identified. Areas of blooming are seen in SWI images.
Retroverted-retroflexed uterus with intrauterine contraceptive device.
Case Discussion
Ovarian mature cystic teratoma is the most common ovarian neoplasm in women in the childbearing period. It has a characteristic fat component that is confirmed on MRI by complete suppression of signal on fat-suppressed sequences. Blooming in SWI sequence may be due to the presence of calcifications.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.