Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome with microhaemorrhage (importance of susceptibility-weighted imaging)
Updates to Case Attributes
This patient was admitted to hospital which confirmed severe hypertension, she received antihypertensive drugs with subsequent improvement of her mental status.
This case illustrates the importance of Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging in the detection of parenchymal micro-hemorrhage in the setting of PRES syndrome, which would help to increase diagnostic accuracy.
A.M. McKinney et al, described the importance of SWI in the detection of micro-hemorrhagic foci in PRES syndrome. They demonstrated in their case study that SWI showed a higher rate of micro-hemorrhagic foci than previously described. They also suggested that those micro-hemorrhagic foci are not correlated with the patient's clinical severity, the MRI imaging severity/extent of edema for PRES syndrome, the presence of DWI-positive findings, or the presence of enhancement on T1WI. Additionally, most micro-hemorrhagic foci appear to persist on long-term follow-up.
They presumed that those micro-hemorrhagic foci could be attributed to o endothelial cell dysfunction.
Updates to Study Attributes
Right pareito-occipital subcortical white matter abnormal signal eliciting high signal on T2 & FLAIR WI. CorrespondigCorresponding subtle gyral diffusion restriction is noted, yet with no significant post contrast enhancement. On SWI, there are corresponding parenchymal multiple innumerable micro-hemorrhagic foci. Similar patches of abnormal signal are seen at the right thalamic pulvinar and the pons.
Small artery disease with bilateral centrum semiovale chronic ischmic foci.
Diffuse brain atrophic changes.
- Based on the radiological findings mainly the posterior distribution, the gyral subtle diffusion restriction and importantly the multiple parenchymal micro-hemorrhagic foci; posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) was considered.
Image MRI (DWI) ( update )
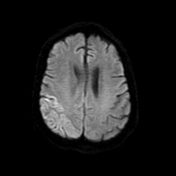
Image MRI (T1 C+) ( update )
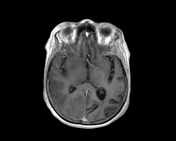
Image MRI (ADC) ( update )
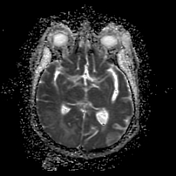
Image MRI (FLAIR) ( update )
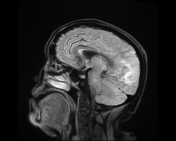
Image 9 MRI (T1 C+) ( create )





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.