Presentation
Previously, she was operated on for carpal tunnel syndrome. Mild, recurring symptoms.
Patient Data
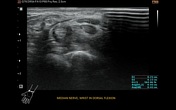

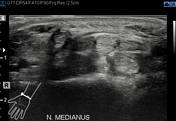

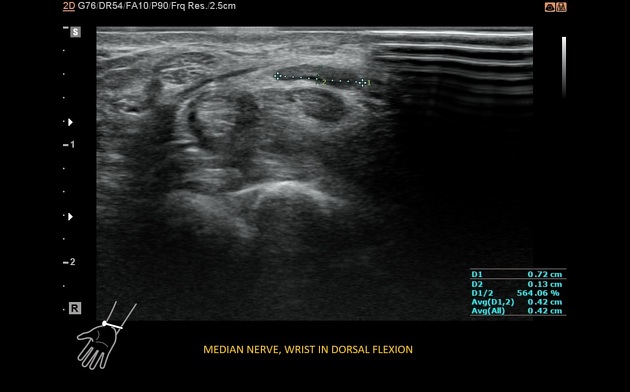
At the anatomic wrist position, palmar bowing of the flexor retinaculum was visible, as was distal median nerve flattening and slight cross-section enlargement.
Dynamic examination showed normal nerve position and cross-section appearance in volar flexion. During dorsal flexion, the median nerve moved to the anteromedial, between the flexor retinaculum and the flexor tendons, and flattened. The retinaculum looked blurred but continuous despite the previous operation.
Case Discussion
The previous operation was performed due to carpal tunnel syndrome. Recurring mild symptoms indicated compression of the nerve. Dynamic ultrasound showed wrist position-dependent median nerve location and flattening, confirming nerve compression and recurring carpal tunnel syndrome.
Reoperation was done, confirming the scarring of the area.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.