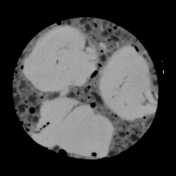

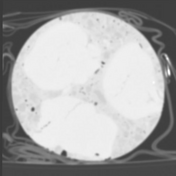



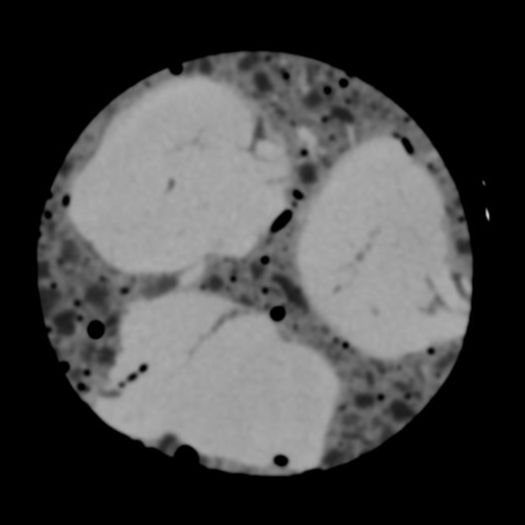
A slab of red sausage or blood sausage with lots of fat globules or cubes and some air bubbles was investigated with a dual-energy CT scanner.
It seems that one can differentiate the protein-rich muscle contents (orange) from the surrounding black pudding (purple) with the fat globules (blue) in the electron density image.
Image Courtesy: Ines Lischka
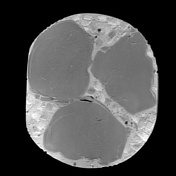








"Look at these contents. No wonder people get high cholesterol from this."
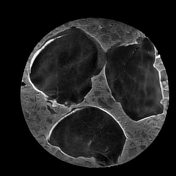
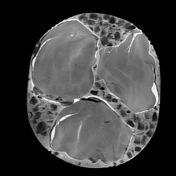
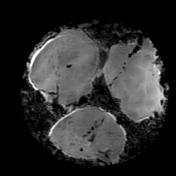
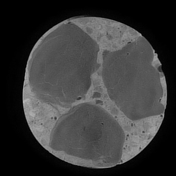
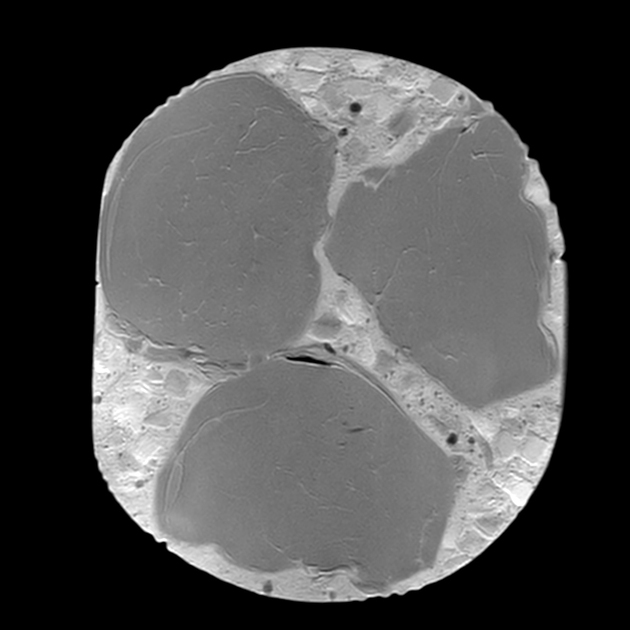
In the Dixon sequence, the intracellular fat content can be appreciated by the signal drop in the in-phase and out-of-phase images and the cubes of macroscopic fat can be nicely seen as squares of high-signal intensity in the fat image of the T1 Dixon sequence. Contents with a high amount of water are hyperintense on the T1 Dixon water image.
Courtesy: Ines Lischka
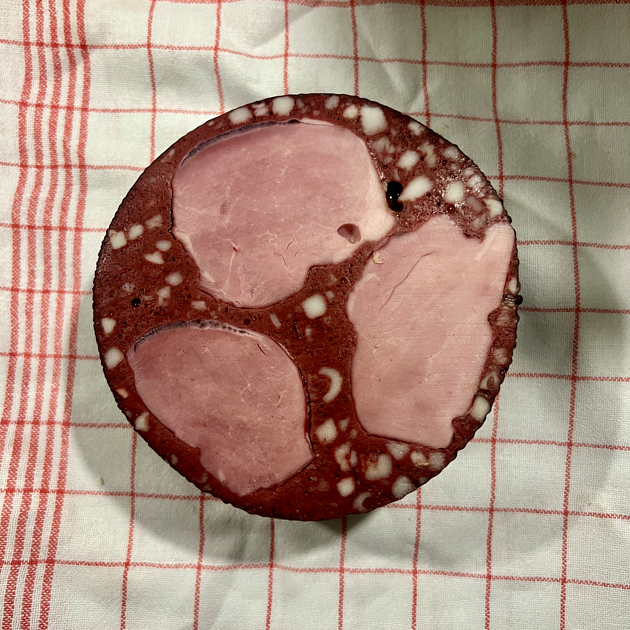

A photo of the red sausage specimen for proof.
Source: original photo created by Joachim Feger
Case Discussion
This is a case of red sausage or blood sausage, the Germans call it "Rotwurst" or "Blutwurst" examined with a dual-energy CT scanner and then on MRI.
You can draw any conclusion you want from this study.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.