Presentation
Right shoulder pain.
Patient Data
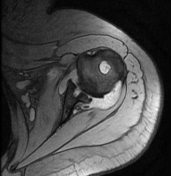

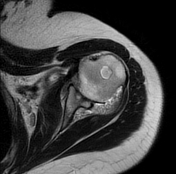

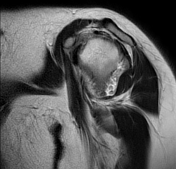

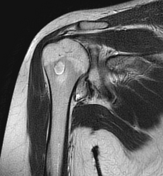

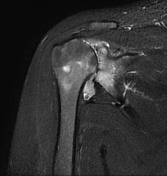

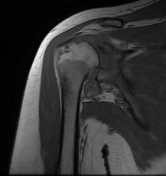

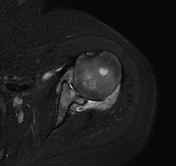

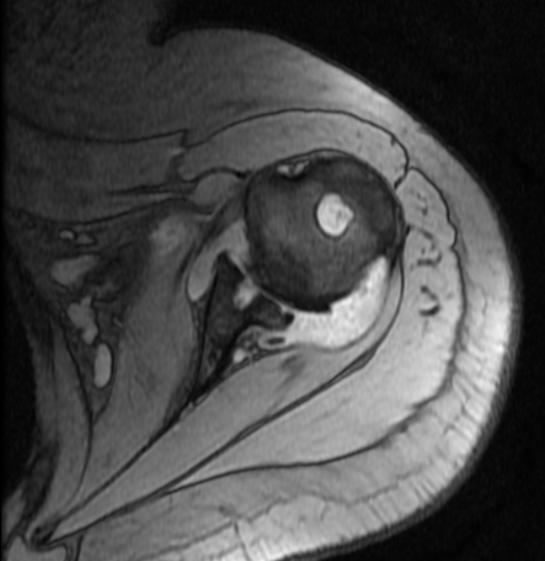
Diffuse circumferential synovial thickening with rice bodies associated with mild joint effusion.
Arthropathic changes of the glenohumeral joint evident by narrowing of its joint space, subchondral marrow degenerative changes and pseudocystic changes.
Diffusely attenuated glenoid labrum.
Opinion: Findings are impressive of Rheumatoid arthritis.
Anti CCP Abs: 104 IU/mL (Ref 0-5)
Rheumatoid factor: 32 IU/mL (Ref 0-20)
25-Hydroxycolecalciferol Vitamin D: 13 ng/mL (Moderate deficiency)
Case Discussion
Features of rheumatoid arthritis best demonstrated with MRI include :
synovial hyperaemia: an indication of acute inflammation
synovial hyperplasia (rice bodies)
pannus formation
decreased thickness of cartilage
-
subchondral cysts and erosions:
-
MRI is much more sensitive than radiography
it is thought that subchondral cysts in rheumatoid arthritis eventually progress to erosions (i.e. constitute "pre-erosions")
contrast enhancement may distinguish erosions or pre-erosions from degenerative subchondral cysts
-
juxta-articular bone marrow oedema
joint effusions




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.