Presentation
The patient presented with seizures, reduced vision, and abnormal hormonal lab results.
Patient Data
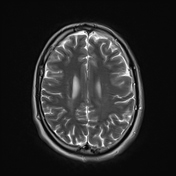

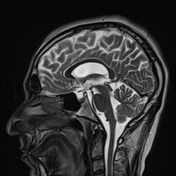

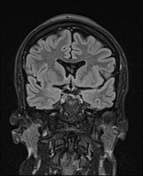

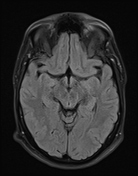

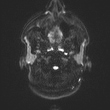

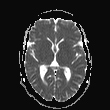


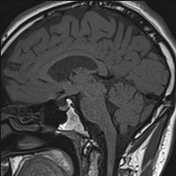

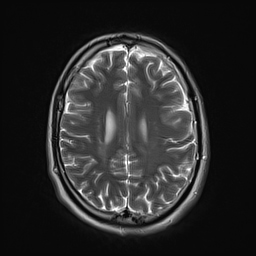
The septum pellucidum is absent, a low position of the fornix.
Squaring of the frontal horns with inferior pointing (Best appreciated on Coronal T2 WI)
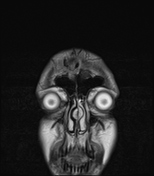
Hypoplastic both optic nerves and chiasma. (Bilateral ONH)
Hypoplasia of the anterior pituitary and infundibulum.
An ectopic posterior pituitary gland located at the hypothalamic region.
The olfactory grooves and nerves are normal on both sides.
Bilateral periventricular frontoparietal altered signal foci of a high T2 and FLAIR, arranged in parallel patterns.
Bilateral posterior parietal peri-trigonal regions altered signal rims are capping both lateral ventricles.
Case Discussion
Septo-optic dysplasia (SOD) is a rare congenital brain anomaly that is considered part of the holoprosencephaly spectrum.
Our case presented clinically with seizures, visual impairments, and signs of pituitary dysfunction.
The key MRI findings of SOD in our case include:
inferior pointing and squaring appearance of the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles
hypoplasia of the optic nerves (bilateral ONH)
hypoplasia of the anterior pituitary and infundibulum
Other MRI findings indicative of SOD that are absent in our case include:
cortical formation abnormalities (including schizencephaly and polymicrogyria), which is then called septo-optic dysplasia PLUS
hypoplasia of the olfactory nerves, which is then called Kallman syndrome
fused hypothalamus
hypoplastic anterior falx
hypogenesis or agenesis of the corpus callosum
a white matter abnormality and/or reduction in normal white matter volume
hypertelorism
Further endocrinological, and ophthalmological follow-up should be recommended for patients with that condition.
Case co-author: Dr Sally Aziz, Nasser institute hospital for research and treatment, Egypt




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.