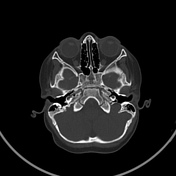
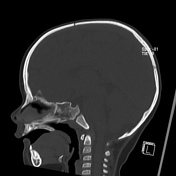
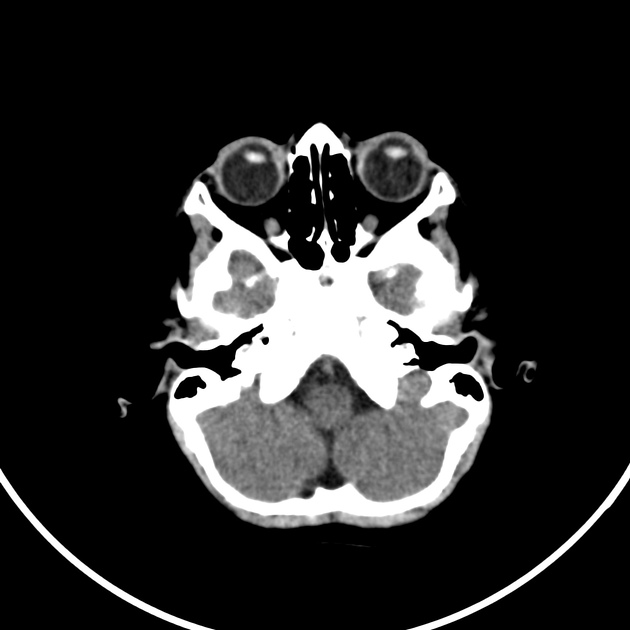
Q: Which of the following findings is visible in the clivus of the present patient – bone destruction, fracture, calcification, or synchondrosis?
show answer
A: Synchondrosis between the basiesphenoid and basiocciput ossification centers, called spheno-occipital synchondrosis.
Q: Which synchondroses are present along the midline in the cranial base?
show answer
A: The synchondroses along the midline in the cranial base are spheno-ethmoidal, intersphenoid, and spheno-occipital synchondroses.
Q: What are the characteristics of spheno-occipital synchondroses?
show answer
A: The spheno-occipital synchondrosis is present in the cranial base. It constitutes a cartilaginous union between the sphenoid bone anteriorly and the basilar portion of the occipital bone posteriorly. It contributes to craniofacial growth and defines the final shape of the craniofacial development by its relation with upper and lower jaws. Spheno-occipital synchondrosis is also related to dentoalveolar development.
Q: In which age group (childhood, youth, adult, Elderly) does the closure of the spheno-occipital synchondrosis usually occur?
show answer
A: There is wide variability in the age of the closure of the spheno-occipital synchondrosis; however, it usually closes in adolescent age groups, near puberty, but occasionally it may persist until age 17 – 25. The fusion occurs first at the superior border and proceeds to the inferior wall.
Q: What is the relationship between puberty onset and spheno-occipital synchondrosis closure?
show answer
A: It seems that there is a relationship between puberty and the beginning of the menarche with spheno-occipital synchondrosis closure, indicating an association with hormonal changes in the adolescent.








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.