Presentation
Bilateral conjunctival whitish fatty lesions.
Patient Data
Age: 70 years
Gender: Male
From the case:
Subconjunctival fat prolapse






Show annotations
Download
Info
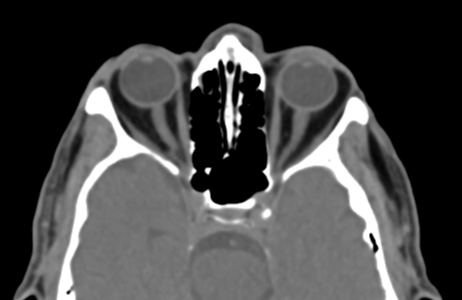
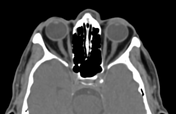
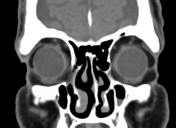
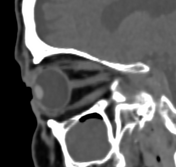
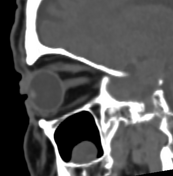
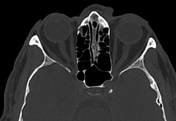
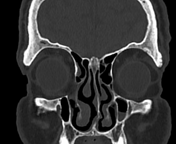
Bilateral conjunctival epibulbar lesions of fat density. They are smoothly abutting the related lateral aspect of the globe with extension to the intra-orbital fat.
Case Discussion
Subconjunctival fat prolapse is an acquired herniation of intraconal fat due to the weakening of the Tenon capsule by normal ageing, surgery, or trauma. It presents clinically with a fat-containing epibulbar mass in the lateral canthal area.
It should be differntiated from orbital dermolipoma which occurs in younger age group and show non connection with the intra-orbital fat.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.