Presentation
Upper limb ischaemia, numbness on abduction
Patient Data
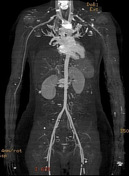
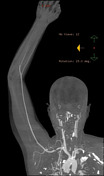
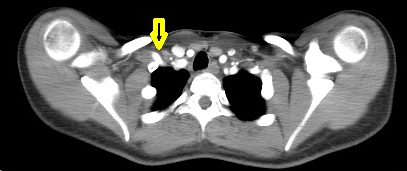
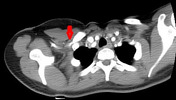
The study was performed with the arm down by the patient’s side and repeated with it raised above the patient’s head. There is a string-like narrowing of the right subclavian artery (arrows) due to the right cervical rib when the arm is raised.
Compare the artery calibre with arm aside (yellow arrow) to it with arm raised (red arrow).
Case Discussion
Thoracic outlet syndrome is the term that refers to compression of the neurovascular bundle at the thoracic inlet (the term ‘thoracic outlet syndrome’ is a misnomer). The syndrome can be classified into three subgroups: venous, arterial and nervous.
It is treated by resection of the cervical rib or fibrous band that is causing the problem. Thrombolysis could be considered in acute thrombosis.
Key points: Thoracic outlet syndrome occurs at one of three sites: (a) the interscalene space (just above the medial first anterior rib); (b) the costoclavicular triangle; (c) the subcoracoid space.
A Pancoast tumour can result in similar symptoms and should be excluded.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.