Presentation
Wrist pain
Patient Data
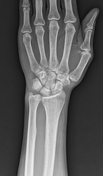
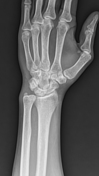
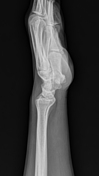
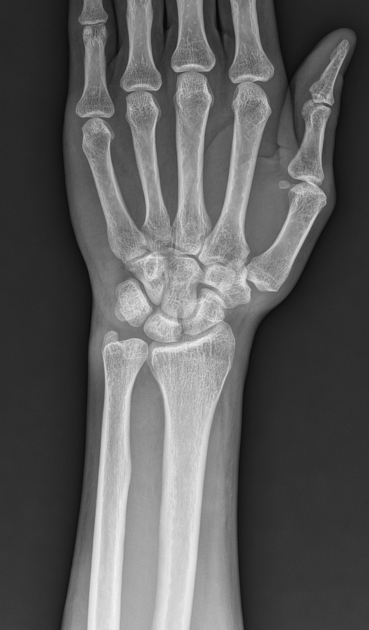
Positive ulnar variance with associated mild subcortical pseudocystic changes of the ulnar aspect of the lunate bone.
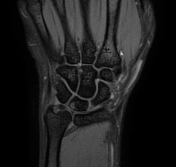

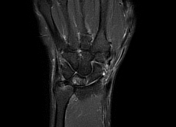

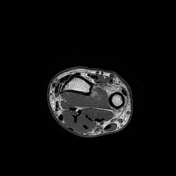

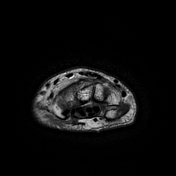


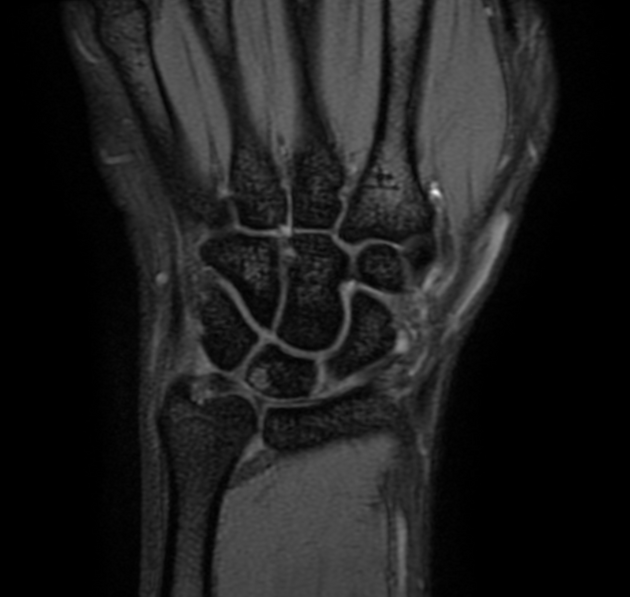
Positive ulnar variance with associated subcortical pseudocystic changes of the ulnar aspect of the lunate bone and underlying lunate bone mild marrow edema signal eliciting high STIR signal. Patchy bone marrow edema of the opposing ulnar bone distal segment.
The triangular fibrocartilage central segment shows an intrasubstance high T2/STIR signal with no evidence of complete interruption.
Mild radio-ulnar joint effusion.
Tenosynovitis of the extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon with no fiber interruption.
Mild intercarpal joint effusion with related mild synovial thickening.
Case Discussion
Positive ulnar variance with associated subcortical pseudocystic changes and marrow edema of the ulnar aspect of the lunate bone and opposing distal ulnar bone as well as triangular fibrocartilage injury is highly suggestive of ulnar impaction syndrome.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.