Presentation
Full term baby with dysmorphic features. Bilateral cloudy cornea (Peters anomaly). Ventricular septal defect (VSD). Cranial ultrasound revealed marked ventricular dilatation.
Patient Data
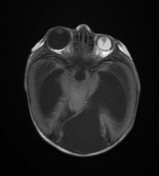

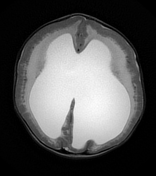

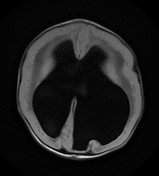

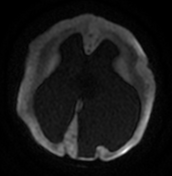

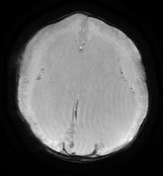

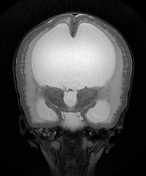

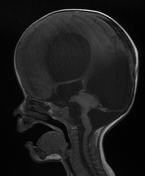

Marked ventricular dilatation, the occipital horn of the left lateral ventricle is herniated to the posterior fossa through a large left tentorial defect causing significant mass effect on the superior aspect of the cerebellum with mild herniation of the right medial occipital lobe through the tentorium suggesting tentorial hypoplasia, absent septum pellucidum, and thin hypoplastic corpus callosum.
Diffuse cobblestone lissencephaly due to neuronal overmigration.
Diffuse abnormal white matter signal with high T2 signal suggesting hypomyelination.
SWI reveals small areas of blooming artifact consistent with hemorrhage.
Severe dysplasia of posterior fossa structures with cerebellar hypoplasia and subcortical innumerable small cysts, vermian hypoplasia, brainstem dysplasia with dorsal kink at the mesencephalic-pontine junction (Z-like appearance), and enlarged dysplastic quadrigeminal plate with obliterated cerebral aqueduct.
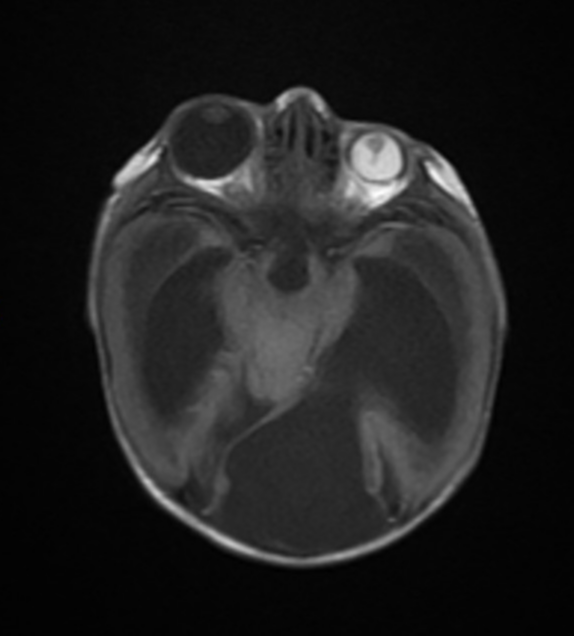
Ocular asymmetry, large right globe (buphthalmos), small left globe (microphthalmos) with its vitreous humerus shows high signal intensity in all sequences suggesting vitreous hemorrhage and band extending from its lens till the optic nerve head suggesting persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous (PHPV) (axial T1, sagittal T1).
Case Discussion
Unfortunately, there's no genetic testing available in this instance. However, a muscle biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. The typical radiological features of Walker-Warburg syndrome which are evident in this case include hydrocephalus, diffuse cobblestone lissencephaly, dorsal kink at the mesencephalic-pontine junction, cerebellar hypoplasia with subcortical innumerable small cysts and ocular anomalies in the form of right buphthalmos and left PHPV.
Walker-Warburg syndrome (WWS) is a rare and severe genetic disorder characterized by a combination of brain, eye, and muscle abnormalities. It is the most severe form of congenital muscular dystrophy and is typically associated with a poor prognosis, often leading to death within the first few years of life.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.